Your Cart is Empty
Customer Testimonials
-
"Great customer service. The folks at Novedge were super helpful in navigating a somewhat complicated order including software upgrades and serial numbers in various stages of inactivity. They were friendly and helpful throughout the process.."
Ruben Ruckmark
"Quick & very helpful. We have been using Novedge for years and are very happy with their quick service when we need to make a purchase and excellent support resolving any issues."
Will Woodson
"Scott is the best. He reminds me about subscriptions dates, guides me in the correct direction for updates. He always responds promptly to me. He is literally the reason I continue to work with Novedge and will do so in the future."
Edward Mchugh
"Calvin Lok is “the man”. After my purchase of Sketchup 2021, he called me and provided step-by-step instructions to ease me through difficulties I was having with the setup of my new software."
Mike Borzage
Design Software History: The Evolution of Design Data Management: From Early File Systems to Cloud-Based Collaborative Solutions
August 24, 2025 9 min read
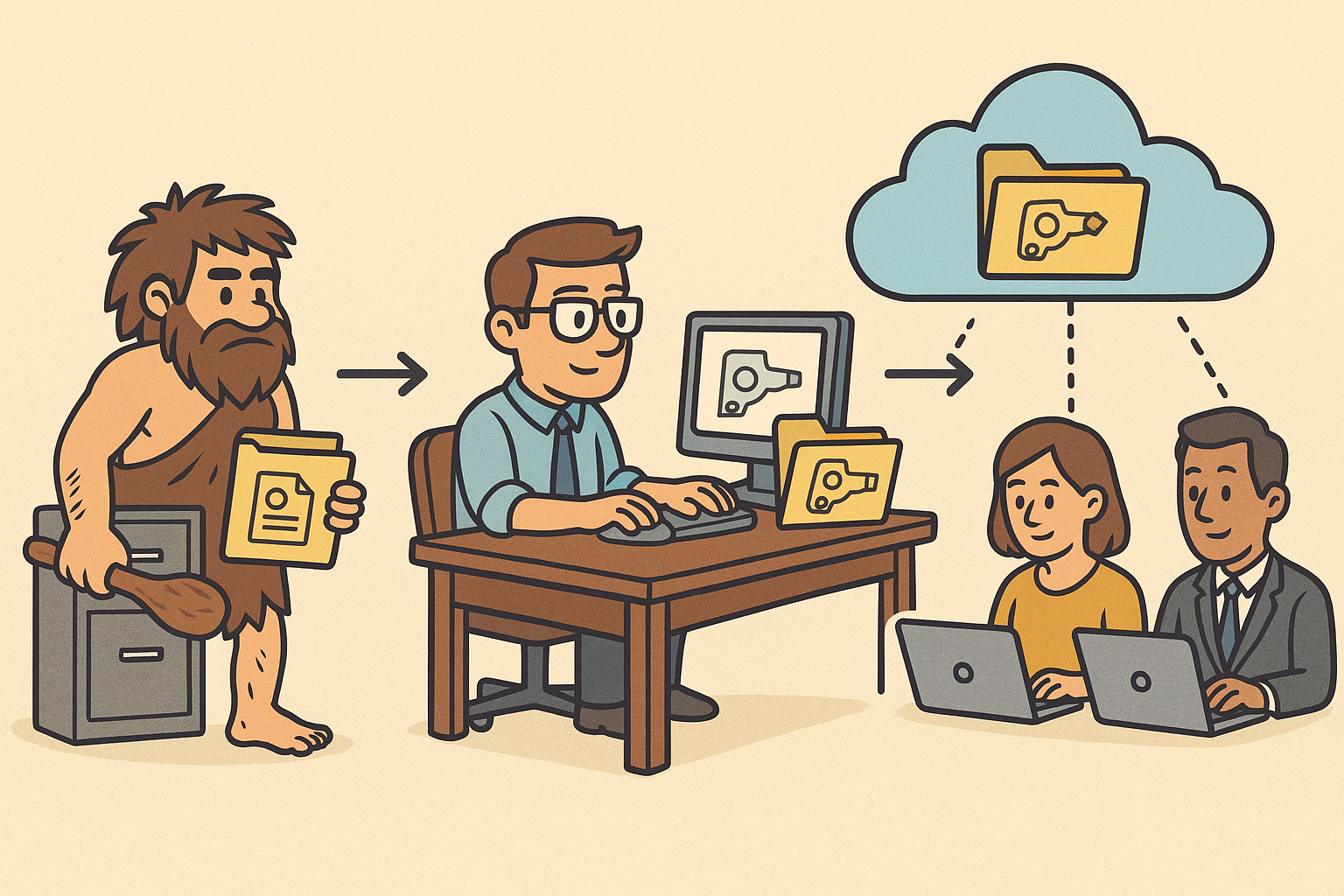

Introduction and Early Beginnings
The evolution of design software has been deeply intertwined with the development of design data management systems. From the inception of early file management methodologies to the current high-performance collaborative environments, managing design data has consistently been a challenging yet crucial part of the design process. In the early stages of computer-aided design (CAD), engineering teams faced significant obstacles when dealing with large sets of design information. These challenges were not simply technical but also organizational, as teams struggled to store, retrieve, and update complex design data within limited computational environments. The industry was burdened with the cumbersome legacy systems that required significant manual intervention, making it difficult to maintain data integrity and operational efficiency. Early file management systems provided a basic framework for data storage, but their limitations were evident as the complexity of design projects grew and the need for structured, scalable data handling became apparent.
Historical Overview of Early File Management
During the formative years of design software, teams relied on rudimentary file management practices, which often involved manual sorting of data and cumbersome indexing methods. Many organizations experimented with digital filing systems that, although innovative at the time, ultimately fell short of meeting the complex demands of design workflows. Notable challenges included:
- Scalability Issues: Early systems struggled to scale as project complexity increased, often leading to data corruption or loss.
- Data Redundancy: Inconsistent data replication across multiple systems resulted in significant redundancies that complicated maintenance and updates.
- Manual Data Handling: The reliance on manual processes not only slowed down project timelines but also introduced a high risk of human error.
As the industry was rapidly transitioning from paper-based to digital systems, design teams had to adapt to increasingly sophisticated file management systems that aimed to automate aspects of data retrieval and update processes. While these early systems marked a significant advancement over traditional methods, they also underscored the need for continuous innovation in data management practices to keep pace with growing technological possibilities and design intricacies.
Milestones in the Evolution of Data Management Systems
The transition from manual file handling to integrated computer-based data management systems represents a pivotal milestone in the history of design software. During this transformative period, the design industry witnessed the gradual replacement of cumbersome manual processes with advanced relational databases and specialized CAD data management tools. The introduction of computer-based systems not only enhanced the efficiency of design processes but also established the groundwork for modern Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) systems. As relational databases emerged, these systems provided structured frameworks that allowed precise storage, retrieval, and maintenance of vast arrays of design data. This era was marked by the evolution of innovative data storage systems that catered to the intricate needs of design workflows, effectively bridging the gap between design visualization and data integrity. In this period, several pioneering companies in engineering software began to integrate administrative data management directly with CAD applications, thereby streamlining workflows and reducing redundancy.
The Emergence of Relational Databases
Relational databases played an instrumental role in structuring design data and ushering in a more organized approach to data management. These databases helped design teams overcome the limitations of earlier systems by:
- Allowing efficient indexing of design elements and metadata
- Enabling rapid retrieval of relevant data through structured queries
- Providing a scalable framework that could adapt to growing design complexity
This transformation was spearheaded by early innovators in software development who understood the critical importance of data structure. Engineers at companies such as IBM, Dassault Systèmes, and Siemens PLM Software contributed significantly to these advances, integrating relational databases with CAD-specific functionalities. This innovation enabled seamless linkage between design elements, changes, and revisions. The resulting synergy between relational database systems and CAD workflows not only enhanced productivity but also laid the foundation for more complex design data environments in the future, thereby adjusting the industry's standards for data integrity and operational efficiency.
Integration of CAD-Specific Data Management
CAD-specific data management systems emerged as a natural progression in the evolution of design data handling. These systems were tailored for the unique demands of the design environment and worked to integrate data management features directly into design software. The integration included functionalities such as version control, lifecycle management, and intelligent data retrieval geared specifically towards bridging the gap between the design process and data oversight. This resulted in a significant reduction of errors and improved overall workflow consistency. The specialized nature of these systems allowed for a more intuitive organization of design components while facilitating efficient collaboration, ensuring that every aspect of the design process was tracked accurately.
Integration with Modern Design and Collaborative Workflows
The leap from isolated data management systems to integrated collaborative environments has fundamentally reshaped the way design software operates. Over the past few decades, the design industry has embraced networked environments, which have proved especially transformative through the adoption of cloud computing and real-time collaborative tools. Modern design data management is now intrinsically linked with collaborative frameworks that support remote work, enabling teams to work together seamlessly regardless of geographical distances. This integration has revolutionized traditional workflows, allowing multiple stakeholders to access, review, and modify design data concurrently. As globalization accelerates and design teams become increasingly dispersed, the need for a common data management platform has become critical to ensure both data integrity and operational efficiency. The most influential modern data management systems have capitalized on interoperability standards, ensuring that design software can exchange vital information efficiently while minimizing the risk of data mismanagement.
Impact of Networked Environments and Cloud Computing
Advances in networked environments and cloud computing have propelled design data management to new heights. The integration of cloud-based platforms has allowed for:
- Global Collaboration: Team members from around the world can access shared data repositories in real time.
- Enhanced Security and Data Integrity: Modern cloud services focus on stringent security protocols and robust backup systems, ensuring data remains accurate and protected.
- Streamlined Workflows: Centralized data repositories facilitate improvements in project management and version control.
These advancements have directly contributed to the development of integrated collaborative frameworks that form the backbone of modern PLM systems. The fusion of design data management with cloud computing has also given rise to intelligent data retrieval systems that leverage automation and smart algorithms. Companies like Autodesk, PTC, and Bentley Systems have been instrumental in driving these innovations, continually refining the way design data is managed, shared, and maintained across diverse platforms. The evolution of these technologies underscores the industry's commitment to overcoming legacy challenges and adapting to an increasingly digital and interconnected world.
Transformation Through Collaborative Tools and PLM Systems
One of the most significant shifts in the evolution of design data management pertains to the integration of collaborative tools with comprehensive PLM systems. These systems were designed to manage not only the visual and technical aspects of design data but also the entire lifecycle of a product—from concept through development, production, and eventual retirement. The incorporation of these tools enabled design teams to reduce miscommunications, keep track of real-time updates, and maintain consistent datasets even as projects evolved. The transformation was further bolstered by developments in standards for interoperability, which ensured that disparate design software systems could work together smoothly. With the advent of collaborative platforms, designers began experiencing uninterrupted workflows that minimized the risk of data loss while ensuring that every revision was meticulously recorded and easily accessible for future reference. These collaborative tools have become indispensable in modern design practices, setting new benchmarks in efficiency and innovation.
Current Trends, Challenges, and Future Directions
Today, design data management continues to evolve under the influence of emerging technologies and shifting organizational demands. As security, data integrity, and efficiency rise to the forefront of industry concerns, design software companies are constantly innovating to address these areas. Recent trends have included the deep integration of blockchain technology to enhance data security, as well as the leveraging of artificial intelligence for smarter data organization and retrieval processes. These innovations are aimed at overcoming the inherent challenges faced by large organizations that manage complex, multi-faceted design datasets. Despite these advancements, challenges such as system integration difficulties, data migration issues, and maintaining interoperability across multiple platforms still persist. The demand for continuous, real-time updates and ever-higher levels of data security means that the design software industry must remain agile in adapting to new technological frontiers while addressing the legacy constraints imposed by older systems.
Evolution of Security and Blockchain in Design Data Management
Security and data integrity have always been pivotal concerns for organizations engaged in large-scale design projects. More recently, the advent of blockchain technology has brought a novel approach to tackling these issues. Blockchain offers a decentralized system that ensures every transaction and change in design data is recorded in an immutable ledger, significantly reducing the possibility of data tampering. Key benefits of integrating blockchain within design data management include:
- Decentralized security protocols that protect data against unauthorized modifications
- Transparent audit trails ensuring traceability of every modification
- Enhanced trust among stakeholders through secure, verifiable records
This transformative approach is complemented by trends in AI-powered data organization. These smart systems enable rapid categorization and retrieval of data, ensuring that the ever-increasing volume of design information can be managed effectively. Research into integrating AI with legacy systems is a critical area, aiming to create interfaces that are both intelligent and intuitive. As a result, the future of design data management is expected to be characterized by a blend of high-security measures with user-friendly, AI-driven interfaces. The innovations emerging in this area are expected to mitigate many of the issues that have historically plagued large organizations while paving the way for more robust, efficient design systems.
Challenges and Future Directions in Data Management
Even with the introduction of these advanced technologies, several challenges continue to confront large organizations. One of the most significant is the maintenance and updating of vast, heterogeneous volumes of data that are spread across multiple platforms. Organizations often struggle with:
- Data Migration: Moving data from legacy systems to modern platforms can be cumbersome and fraught with error.
- System Integration: Achieving a harmonious data environment when different systems are involved has proven to be a complex task.
- Scalability: As design projects continue to grow in scale, maintaining performance and speed while handling large data loads remains a major challenge.
To address these issues, ongoing research into AI-powered data organization and concrete advancements in blockchain-based security is paving the way for future breakthroughs. Collaboration among industry giants such as Siemens, Autodesk, and PTC is fueling this progression. Future advancements are expected to enable more dynamic and adaptable systems that can seamlessly integrate historical data with emerging technologies, ensuring a smooth transition into next-generation design workflows. The continuous integration of these technologies, combined with a relentless drive for data security and efficiency, defines the future direction of design data management. It is likely that future systems will not only solve current challenges but also set new paradigms for data integrity, security, and collaborative efficiency in design projects around the world.
Conclusion
The historical trajectory of design data management reveals a landscape marked by constant innovation, significant challenges, and transformative change. This journey began with the early file management systems that laid the groundwork for the digital storage of design data, evolved through the development and integration of relational databases and CAD-specific management tools, and culminated in the modern era where cloud computing, blockchain, and AI-powered technologies converge to revolutionize collaborative workflows. Each stage of this evolution has been driven by the relentless pursuit of data integrity, operational efficiency, and enhanced security. The collaboration across leading companies and influenced by pioneering innovators has set benchmarks, establishing robust protocols for managing increasingly complex design datasets.
Reflection on Technological Shifts in Data Management
Understanding the historical milestones in design data management provides invaluable insights for future innovation. The technological shifts—from manual processes to fully integrated, cloud-based systems—highlight the importance of adaptability and forward-thinking strategies. Alongside industry contributions from companies like Dassault Systèmes, Siemens, and Autodesk, significant refinements in data handling have consistently addressed the challenges of scalability, interoperability, and security. As modern systems continue to integrate more advanced technologies, such as AI for smart retrieval and blockchain for immutable data tracking, the future of design data management appears well-poised for further evolution. This evolution serves as a strong reminder that the challenges dealt with in earlier eras laid the technical and conceptual foundation for the robust, multifaceted systems in place today.
Final Thoughts on Future Innovation
Looking forward, it is evident that the future of design data management will likely be defined by an even greater degree of integration between emerging technologies and traditional design practices. Innovations in AI, combined with the reliability of blockchain and cloud computing, will drive the next wave of transformation. This transformation will be critical in addressing the perennial challenges faced by large organizations, such as data migration, system integration, and scalability. Investments in these areas will not only streamline operations but also set new standards for data accuracy and collaborative efficiency in global design projects. As companies continue to collaborate and refine their processes, the knowledge gained from historical milestones will inspire further innovations that promise to optimize design workflows and unlock new potentials in design software development. The lessons learned from the past assure us that every challenge brings an opportunity for ingenuity, creating a pathway towards more efficient and secure design processes in the future.
Also in Design News

Revit Tip: Standardize Annotation Crops and Borders with View Templates
January 23, 2026 2 min read
Read More
V-Ray Tip: Reuse Single Light Cache Prepass for Camera-Only Animation
January 23, 2026 2 min read
Read MoreSubscribe
Sign up to get the latest on sales, new releases and more …



