Your Cart is Empty
Customer Testimonials
-
"Great customer service. The folks at Novedge were super helpful in navigating a somewhat complicated order including software upgrades and serial numbers in various stages of inactivity. They were friendly and helpful throughout the process.."
Ruben Ruckmark
"Quick & very helpful. We have been using Novedge for years and are very happy with their quick service when we need to make a purchase and excellent support resolving any issues."
Will Woodson
"Scott is the best. He reminds me about subscriptions dates, guides me in the correct direction for updates. He always responds promptly to me. He is literally the reason I continue to work with Novedge and will do so in the future."
Edward Mchugh
"Calvin Lok is “the man”. After my purchase of Sketchup 2021, he called me and provided step-by-step instructions to ease me through difficulties I was having with the setup of my new software."
Mike Borzage
Design Software History: Augmented Reality in Design Visualization: Historical Milestones and Future Prospects
June 03, 2024 4 min read
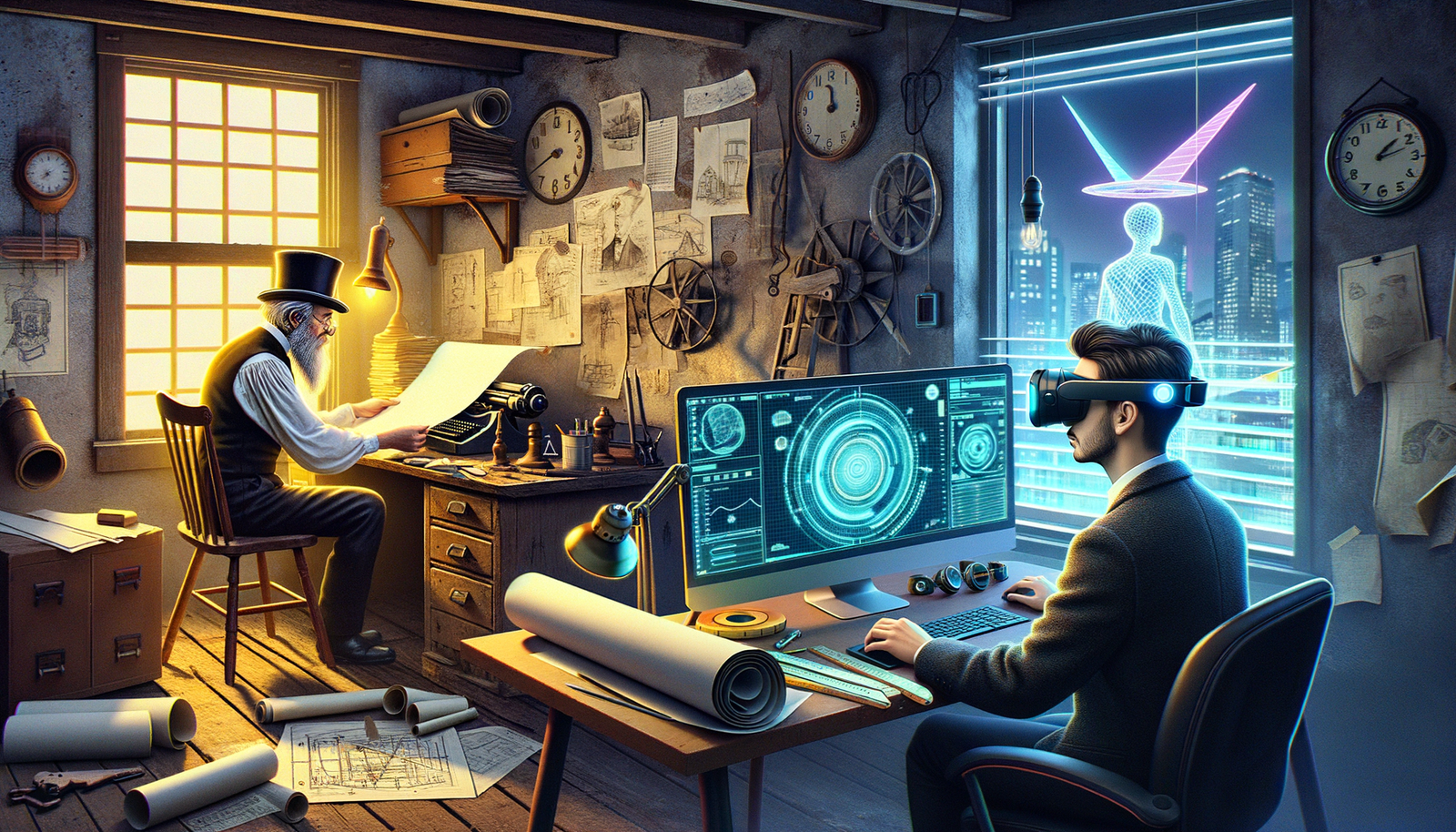


Introduction to Augmented Reality (AR) in Design
Augmented Reality (AR) is a technology that superimposes digital information onto the real world, offering an enriched view that blends physical and virtual elements. The evolution of AR began with early conceptualizations in the 1960s and has since matured into a sophisticated tool used across various industries, including design.
The significance of AR in design visualization lies in its ability to enhance the design process by providing a more immersive and interactive experience compared to traditional methods. Unlike conventional design visualization, which often relies on 2D drawings or static 3D models, AR enables designers to visualize and manipulate digital objects within a real-world context, leading to improved understanding and communication of design concepts.
Historical Milestones and Key Innovations
Early Adoption and Pioneers
The journey of AR began with the pioneering work of Ivan Sutherland, who developed the first Head-Mounted Display (HMD) system in the 1960s. This early system, known as the "Sword of Damocles," laid the groundwork for future AR technologies by allowing users to view simple wireframe models superimposed on their real-world view.
Throughout the following decades, advancements in computing power and display technologies paved the way for more sophisticated AR systems. Companies such as Boeing and NASA were among the early adopters, utilizing AR for complex visualization and simulation tasks.
Technological Advancements
The development of AR hardware has seen significant progress, with devices like the Microsoft HoloLens and Magic Leap offering advanced capabilities for immersive design visualization. These devices feature high-resolution displays, precise tracking systems, and powerful processing units, enabling seamless integration of digital and physical environments.
On the software side, platforms such as Unity and Unreal Engine have revolutionized AR development by providing robust tools for creating interactive AR experiences. These platforms support a wide range of design applications, from architectural visualization to product prototyping, making AR more accessible to designers and developers.
Applications of AR in Various Design Fields
Architectural Design and Urban Planning
In architectural design and urban planning, AR enables designers to visualize building designs in real environments, offering a more accurate representation of how structures will interact with their surroundings. This capability is particularly useful for site analysis and client presentations, where stakeholders can view and assess proposed designs in a more tangible and immersive manner.
Some of the ways AR is utilized in this field include:
- Site Analysis: AR allows architects to overlay digital models onto physical sites, facilitating the assessment of design feasibility and environmental impact.
- Client Presentations: AR enhances client presentations by providing an interactive experience where clients can explore and interact with design concepts.
Product and Industrial Design
AR is also transforming product and industrial design by streamlining the prototyping and iteration phases. Designers can use AR to visualize and manipulate digital prototypes in real-world contexts, reducing the need for physical prototypes and accelerating the design process.
Applications of AR in product design include:
- Prototyping: AR enables designers to create and test digital prototypes in real-time, allowing for rapid iteration and refinement.
- Product Visualization: Companies use AR to visualize products in various settings, aiding in design validation and marketing efforts.
Engineering and Manufacturing
In engineering and manufacturing, AR plays a crucial role in enhancing assembly instructions, maintenance, and quality control processes. By overlaying digital information onto physical components, AR helps engineers and technicians perform complex tasks with greater accuracy and efficiency.
Examples of AR applications in this field include:
- Assembly Instructions: AR provides step-by-step guidance for assembling complex machinery, reducing errors and improving productivity.
- Maintenance and Quality Control: AR aids in identifying defects and performing maintenance tasks by overlaying diagnostic information onto physical objects.
Future Prospects and Challenges
Potential Advancements
The future of AR in design visualization holds exciting possibilities, with advancements in AR hardware and software expected to drive further innovation. Emerging technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) are likely to integrate with AR, creating more intelligent and interconnected design environments.
Future advancements may include:
- Enhanced Hardware: Continued improvements in display resolution, processing power, and battery life will make AR devices more powerful and user-friendly.
- AI Integration: AI-powered AR applications could offer advanced features such as real-time object recognition, predictive modeling, and automated design suggestions.
- IoT Connectivity: The integration of AR with IoT devices will enable seamless interaction between digital models and physical objects, enhancing design validation and monitoring.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its potential, AR faces several challenges that must be addressed to realize its full impact in design visualization. These challenges include:
- Technical Challenges: Hardware limitations, such as limited field of view and battery life, and software compatibility issues can hinder the adoption of AR technologies.
- Practical Challenges: User acceptance, high costs, and the need for specialized training can pose barriers to widespread AR implementation.
- Ethical and Security Considerations: The use of AR in design raises ethical questions related to privacy, data security, and the potential for misuse of digital information.
Conclusion
In summary, Augmented Reality has made significant contributions to design visualization, offering a powerful tool for enhancing the design process across various fields. From architectural design to product development and engineering, AR has the potential to transform how designers visualize, iterate, and communicate their ideas.
As we look to the future, continued exploration and innovation in AR technology will be crucial in unlocking its full potential. Designers and developers are encouraged to embrace AR in their workflows, leveraging its capabilities to create more immersive, interactive, and efficient design solutions.
Also in Design News
Design Software History: Topology in CAD: Manifoldness, Genus, and the Earliest B‑Rep Formalisms
January 02, 2026 14 min read
Read MoreSubscribe
Sign up to get the latest on sales, new releases and more …




