Your Cart is Empty
Customer Testimonials
-
"Great customer service. The folks at Novedge were super helpful in navigating a somewhat complicated order including software upgrades and serial numbers in various stages of inactivity. They were friendly and helpful throughout the process.."
Ruben Ruckmark
"Quick & very helpful. We have been using Novedge for years and are very happy with their quick service when we need to make a purchase and excellent support resolving any issues."
Will Woodson
"Scott is the best. He reminds me about subscriptions dates, guides me in the correct direction for updates. He always responds promptly to me. He is literally the reason I continue to work with Novedge and will do so in the future."
Edward Mchugh
"Calvin Lok is “the man”. After my purchase of Sketchup 2021, he called me and provided step-by-step instructions to ease me through difficulties I was having with the setup of my new software."
Mike Borzage
Transforming Design Workflows with Finite Element Analysis Integration
March 29, 2025 11 min read


In the rapidly evolving field of design and engineering, integrating advanced computational tools has become essential for innovation and competitiveness. One such tool that has significantly impacted the way designers and engineers approach complex problems is Finite Element Analysis (FEA). By enabling detailed simulations and analyses of how designs will perform under various conditions, FEA has transformed traditional workflows, leading to more accurate, reliable, and optimized products. This article delves into the understanding of FEA, its integration into design workflows, and the myriad benefits and challenges associated with its implementation.
Definition and Fundamentals
Finite Element Analysis (FEA) is a computational technique used to simulate and predict how a product or structure will react to real-world physical effects such as external forces, heat, vibration, fluid flow, and other impacts. By breaking down complex geometries into smaller, manageable finite elements, FEA allows for detailed analysis of each component's behavior under specified conditions. At its core, FEA operates on the principle of discretization, where the entire domain of a structure is divided into a mesh of elements connected at nodes. Mathematical equations governing the physical behavior are applied to these elements, and numerical methods are used to approximate solutions, resulting in a comprehensive understanding of the entire system's performance.
The core principles of FEA involve the application of physics and engineering to predict material behavior, leveraging differential equations that describe various physical phenomena. The method accounts for the properties of materials, boundary conditions, and external influences to simulate scenarios that are often too complex for analytical solutions.
The historical evolution of FEA is rooted in the necessity of solving complex engineering problems that arose during the mid-20th century. Initially developed in the aerospace industry during the 1940s and 1950s to address the challenges of stress analysis in aircraft structures, FEA was a response to the limitations of traditional analytical methods. With the advent of digital computers, FEA methods were refined and expanded, leading to commercial software solutions in the 1970s. Over the decades, continued advancements in computational power and algorithms have made FEA an indispensable tool across various fields, including automotive, civil engineering, biomedical engineering, and consumer product design. Today, FEA is deeply integrated into modern design processes, providing critical insights that inform decision-making and innovation.
Key Applications in Design Software
Finite Element Analysis has widespread applications within modern design software, significantly impacting various engineering disciplines. Some of the primary applications include:
- Structural Analysis: FEA enables engineers to evaluate the mechanical behavior of components and assemblies under different loading conditions. By simulating stresses, strains, and deflections, FEA helps in identifying critical stress points and potential failure regions, allowing for optimization of material usage and structural integrity.
- Thermal and Fluid Dynamics: FEA assists in analyzing heat transfer mechanisms and fluid flow within and around solid structures. Designers can model conduction, convection, and radiation heat transfer, predicting temperature distributions to improve thermal management strategies. Fluid dynamics simulations help in designing efficient pumps, valves, and ventilation systems.
- Vibration and Acoustics: FEA predicts natural frequencies and mode shapes of structures to avoid resonance, excessive vibrations, and noise. It is crucial in ensuring comfort and safety in vehicles, machinery, and buildings by implementing damping mechanisms and structural modifications.
These applications are facilitated by advanced design software that integrates FEA capabilities, allowing for comprehensive simulations within the design environment. By incorporating FEA into the early stages of product development, engineers and designers can iteratively refine their concepts, leading to more innovative solutions and reducing the risk of costly redesigns later in the process. The versatility of FEA in handling various physical phenomena makes it an invaluable tool in modern engineering, bridging the gap between theoretical design and practical application.
Importance of FEA in Modern Design Workflows
The integration of Finite Element Analysis into modern design workflows is pivotal in enhancing the accuracy and reliability of engineering projects. By allowing designers to simulate and analyze the physical behavior of products under various conditions, FEA provides a deeper understanding of how designs will perform in the real world. This predictive capability reduces reliance on assumptions and empirical formulas, leading to more precise and dependable outcomes. The early identification of potential issues through FEA enables teams to address weaknesses in the design phase, significantly reducing the risk of product failure and the costs associated with late-stage modifications or recalls.
Moreover, FEA plays a crucial role in facilitating innovation and complex problem-solving. As products and systems become increasingly sophisticated, traditional analytical methods may fall short in addressing the intricacies involved. FEA empowers engineers to tackle complex geometries, nonlinear material behaviors, and dynamic interactions that were previously challenging to analyze. By providing the tools to explore "what-if" scenarios, FEA encourages experimentation and optimization, leading to innovative solutions that enhance performance, efficiency, and sustainability.
Additionally, the incorporation of FEA into design workflows streamlines the iterative process of design and validation. Engineers can rapidly test multiple design iterations, adjusting parameters and immediately assessing the impacts. This agility accelerates the development timeline and fosters a more proactive approach to problem-solving. The integration of FEA promotes a seamless transition from concept to detailed design, ensuring that analysis is an integral part of the design process rather than an afterthought.
Furthermore, the collaborative nature of modern design environments benefits from FEA by providing a common platform for multidisciplinary teams to interact. Shared insights from FEA simulations can inform decisions across different aspects of a project, aligning mechanical, thermal, and material considerations. This holistic approach enhances the overall quality and cohesiveness of the final product.
Seamless Software Integration
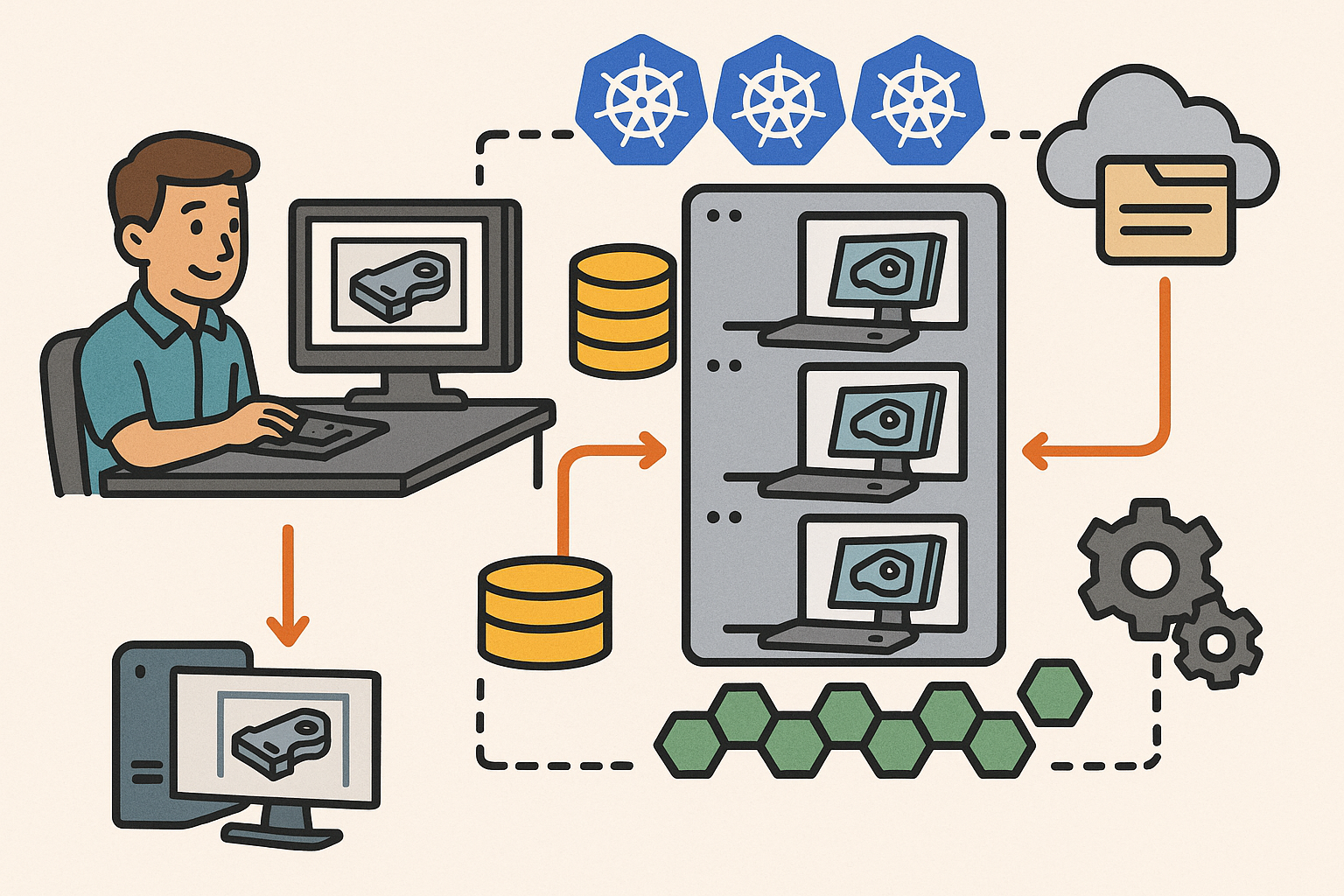
Achieving seamless software integration is essential for maximizing the benefits of Finite Element Analysis in design workflows. One of the primary strategies involves ensuring compatibility between Computer-Aided Design (CAD) tools and FEA software. Integrating these tools allows for a fluid exchange of data, minimizing the time and effort required to prepare models for analysis. This compatibility can be achieved through the use of standardized file formats, such as STEP or IGES, which facilitate the transfer of geometric data without loss of fidelity. However, direct integration within a unified software environment provides an even more efficient solution, eliminating the need for data export and import altogether.
Another strategy is utilizing Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) and plugins to enable smooth data transfer and extend functionality. APIs allow developers to create custom scripts or applications that automate repetitive tasks, tailor the software to specific needs, and enhance interoperability between different programs. Plugins can add specialized features to existing software, bridging gaps between CAD and FEA tools. By leveraging APIs and plugins, organizations can create a more cohesive and tailored workflow, aligning the software capabilities with their unique design and analysis requirements.
Moreover, many modern software solutions offer integrated platforms where CAD and FEA modules are part of the same ecosystem. This integration supports a more streamlined process, where changes in the design model are automatically reflected in the analysis setup. Such synchronization reduces errors associated with model translation and ensures that analyses are always based on the most current design iteration. Real-time feedback and analysis within the design environment enhance efficiency, allowing designers to make informed decisions promptly.
Challenges in software integration often arise from differences in data structures, units, and modeling approaches between CAD and FEA tools. Addressing these issues may require establishing standardized protocols within the organization, training personnel on best practices, and investing in compatible software solutions. Selecting software that supports multi-disciplinary collaboration is also crucial, as it facilitates communication and data sharing among team members from different engineering backgrounds.
Workflow Automation
Workflow automation is a key strategy for enhancing efficiency when integrating Finite Element Analysis into design processes. By automating repetitive tasks and simulations, engineers can significantly reduce the time spent on manual setup and focus more on interpreting results and refining designs. Automation can be achieved through scripting, macros, or utilizing built-in automation tools within FEA software. For example, parameterized models can be set up to automatically adjust geometry, material properties, or loading conditions, and then run simulations without manual intervention. This approach not only saves time but also ensures consistency and reproducibility in analyses.
Streamlining the design-validation cycle is another crucial aspect of workflow automation. In traditional workflows, design and analysis are often sequential steps, which can be time-consuming and prone to delays if iterations are required. By automating the integration between design updates and subsequent simulations, changes made in the CAD model can automatically trigger corresponding FEA analyses. This seamless connection accelerates the feedback loop, allowing designers to rapidly assess the impact of modifications and make informed decisions promptly.
Additionally, automation allows for the implementation of optimization algorithms and design exploration techniques. Engineers can set up studies that vary multiple parameters simultaneously, using techniques like Design of Experiments (DOE) or genetic algorithms to identify optimal design configurations. Automated optimization leverages the computational power of FEA software to explore a wider design space than would be feasible manually, leading to innovative solutions that meet or exceed performance targets.
Automating report generation and documentation is another benefit, ensuring that results are consistently captured and communicated to stakeholders. Templates can be created to automatically compile key findings, visualizations, and data summaries, enhancing collaboration and transparency within the team.
Cloud-Based FEA Solutions
The adoption of cloud-based Finite Element Analysis solutions represents a significant advancement in the way engineering simulations are conducted. Cloud computing offers numerous benefits for FEA, including scalability, cost-effectiveness, and accessibility. One of the primary advantages is the ability to leverage high-performance computing resources without the need for substantial upfront investment in hardware. Complex simulations that require significant computational power can be run more quickly on cloud platforms, reducing processing times from days to hours or even minutes. This scalability allows organizations to handle larger models and more detailed analyses than would be possible with on-premises resources.
Collaboration and accessibility enhancements are also key benefits of cloud-based FEA solutions. Cloud platforms typically offer centralized data storage and management, enabling team members to access simulation models and results from anywhere with an internet connection. This fosters greater collaboration, as engineers, designers, and stakeholders can share insights and provide feedback in real-time. Cross-functional teams can work together more effectively, regardless of geographical location, facilitating a more integrated and agile development process.
Furthermore, cloud-based solutions often include automated updates and maintenance, ensuring that users always have access to the latest software features and security enhancements without the need for manual installations. This reduces the burden on IT departments and minimizes downtime associated with software updates.
Enhanced Design Accuracy and Optimization
Integrating Finite Element Analysis into the design process significantly enhances design accuracy and optimization, leading to superior product performance and reliability. One of the crucial benefits is the ability to identify potential issues early in the design process. By simulating real-world conditions, FEA allows engineers to pinpoint stress concentrations, deformation areas, thermal hotspots, and other critical factors that could lead to failure. Early detection of these issues enables designers to make necessary adjustments before costly prototypes are built or production begins, thereby reducing the risk of product recalls and ensuring compliance with safety standards.
Optimizing materials and structures for performance is another significant advantage of FEA integration. By analyzing how different materials react under various conditions, engineers can select the most appropriate materials that meet the desired strength, weight, cost, and durability criteria. FEA provides insights into material behavior, allowing for the design of lighter, stronger, and more efficient components. Structural optimization techniques, such as topology optimization integrated within FEA tools, enable designers to remove unnecessary material, ensuring that structures are as efficient as possible without compromising integrity.
Cost and Time Efficiency
One of the most significant impacts of integrating Finite Element Analysis into design workflows is the improvement in cost and time efficiency. FEA enables engineers to simulate and analyze designs virtually, which reduces the need for physical prototypes. Traditional design processes often rely heavily on building multiple prototypes to test and refine products, which is both time-consuming and expensive. By utilizing FEA, organizations can minimize the number of physical prototypes required, as virtual simulations provide valuable insights into how the product will perform under various conditions. This shift from physical to virtual testing not only saves material and labor costs but also accelerates the development timeline.
Accelerating the design iteration process is another critical benefit of FEA integration. In a competitive market, bringing products to market quickly is essential. FEA allows designers to rapidly evaluate different design options and make adjustments in real-time. The ability to simulate changes and immediately observe the effects on performance streamlines the iteration process. Engineers can explore a broader range of design alternatives in less time, optimizing designs more effectively than would be possible through physical testing alone.
Improved Decision-Making
Integrating Finite Element Analysis into design workflows greatly enhances improved decision-making by providing comprehensive, data-driven insights. FEA simulations generate detailed quantitative data on how designs will perform under various scenarios, enabling engineers and designers to make informed choices based on empirical evidence rather than assumptions or intuition. Access to precise simulation data allows for better evaluation of trade-offs, such as material selection, weight versus strength considerations, and cost implications, leading to optimized design solutions that meet performance requirements and business objectives.
Furthermore, facilitating multidisciplinary collaboration is a significant benefit of FEA integration. Complex engineering projects often involve teams from different disciplines, including mechanical, electrical, thermal, and manufacturing engineering. FEA provides a common platform where simulations can address various aspects of a design simultaneously. For example, a mechanical engineer can focus on structural integrity while a thermal engineer assesses heat dissipation, all within the same simulation environment. This integrated approach fosters better communication and alignment among team members, ensuring that design decisions consider all relevant factors and that potential conflicts are identified and resolved early in the process.
Technical Challenges
While the integration of Finite Element Analysis into design workflows offers numerous benefits, it also presents several technical challenges that organizations must address. Some of the key challenges include:
- Managing Complex Simulations and Large Datasets: Handling large mesh sizes, high degrees of freedom, and nonlinear material behaviors demands substantial computational resources, including powerful hardware and storage solutions.
- Ensuring Software Compatibility and Interoperability: Integrating various software tools can be difficult due to differences in data formats and modeling methods, potentially leading to inefficiencies and errors in data translation.
To address these technical challenges, organizations can explore solutions such as investing in high-performance computing resources, implementing effective data management systems, and adopting standardized data exchange protocols to enhance interoperability. By addressing computational demands and ensuring software compatibility, organizations can fully leverage the benefits of FEA and enhance their engineering capabilities.
User Adoption and Training
Another significant challenge in integrating Finite Element Analysis into design workflows is user adoption and training. Overcoming the learning curve for designers and engineers is essential to fully realize the benefits of FEA. Advanced FEA software can be complex and may require a deep understanding of simulation principles, material science, and numerical methods. Designers and engineers who are accustomed to traditional design tools may find it challenging to adapt to the technical intricacies involved in setting up simulations, interpreting results, and integrating findings into the design process. This learning curve can lead to resistance to adoption, errors in analysis, and underutilization of the software's capabilities.
Providing adequate training and support resources is crucial to address these challenges. Organizations need to invest in comprehensive training programs that cover both the theoretical foundations of FEA and practical applications within the specific context of their projects. Training can include workshops, online courses, tutorials, and mentorship opportunities. By enhancing the skill sets of the team, organizations empower their personnel to use FEA tools effectively and confidently.
Cost Considerations
Cost considerations represent a key challenge in the integration of Finite Element Analysis into design workflows. Balancing investment in FEA tools with the expected return on investment (ROI) is crucial for organizations, particularly those with limited budgets or smaller scale operations. High-end FEA software often comes with substantial licensing fees, which can be a significant financial burden. Additionally, the need for powerful hardware to run complex simulations adds to the initial investment cost. Organizations must assess whether the anticipated benefits, such as reduced time to market, improved product performance, and lower prototyping costs, justify the expenditure.
Exploring scalable and flexible licensing models is a viable solution to address these cost challenges. Many software providers now offer a variety of licensing options, including subscription-based models, pay-per-use, or cloud-based access. These models allow organizations to scale their investment according to project demands, reducing upfront costs and providing flexibility to adjust resources as needed. For instance, during peak project periods, additional licenses or computing resources can be temporarily acquired to meet increased workloads, without committing to long-term contracts.
Investing in training and skill development also contributes to maximizing ROI. Well-trained personnel can utilize FEA tools more efficiently, reducing errors and improving the quality of analysis. Efficient use of FEA software leads to time savings and better design outcomes, enhancing the overall value derived from the investment.
Conclusion
Integrating Finite Element Analysis into design workflows revolutionizes the way designers and engineers approach product development. FEA empowers teams to enhance accuracy, optimize performance, and accelerate time-to-market by enabling detailed simulations and analyses that inform better decision-making. While challenges such as technical complexities, user adoption, and cost considerations exist, these can be addressed through strategic planning, investment in training, and leveraging modern solutions like cloud computing and flexible licensing. As design software continues to evolve, the seamless incorporation of FEA will remain a pivotal factor in driving innovation and achieving excellence in complex design projects. Organizations that embrace FEA integration stand to gain a competitive advantage, delivering superior products that meet the evolving demands of the marketplace.
Also in Design News
Rhino 3D Tip: True Intersections for Accurate, Repeatable Trim Curves
December 17, 2025 2 min read
Read More
Design Software History: Traceability as a Product Requirement: How Compliance Remade CAD, PDM, and PLM
December 17, 2025 10 min read
Read MoreSubscribe
Sign up to get the latest on sales, new releases and more …