Your Cart is Empty
Customer Testimonials
-
"Great customer service. The folks at Novedge were super helpful in navigating a somewhat complicated order including software upgrades and serial numbers in various stages of inactivity. They were friendly and helpful throughout the process.."
Ruben Ruckmark
"Quick & very helpful. We have been using Novedge for years and are very happy with their quick service when we need to make a purchase and excellent support resolving any issues."
Will Woodson
"Scott is the best. He reminds me about subscriptions dates, guides me in the correct direction for updates. He always responds promptly to me. He is literally the reason I continue to work with Novedge and will do so in the future."
Edward Mchugh
"Calvin Lok is “the man”. After my purchase of Sketchup 2021, he called me and provided step-by-step instructions to ease me through difficulties I was having with the setup of my new software."
Mike Borzage
Digital Prototyping: Revolutionizing Design Efficiency and Innovation in Modern Engineering
November 11, 2024 6 min read


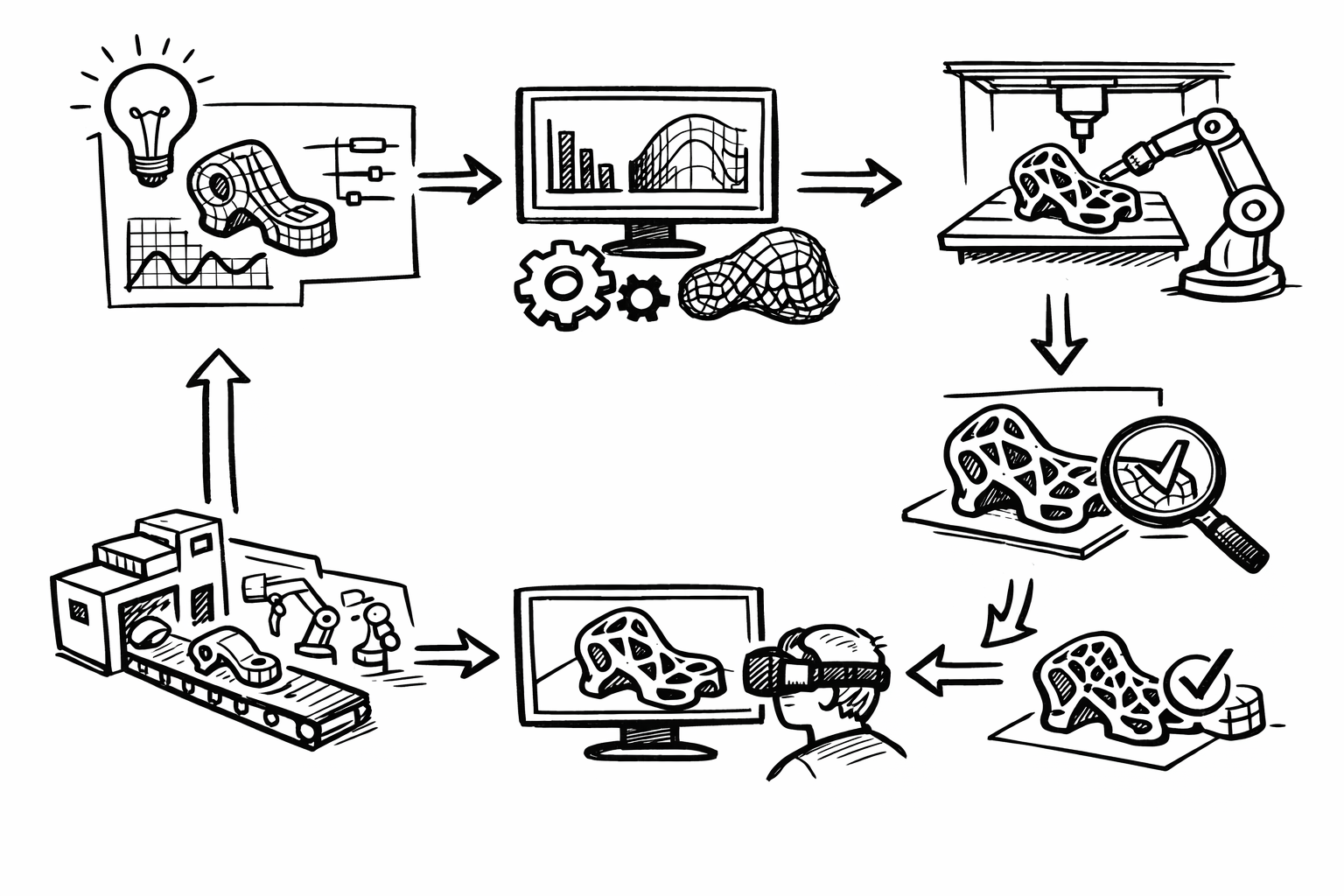
In the rapidly evolving landscape of design and engineering, digital prototyping has emerged as a pivotal component of modern development processes. As industries strive for greater efficiency and innovation, the ability to create and test products virtually offers unparalleled advantages. This approach not only accelerates development timelines but also enhances the quality and performance of the final product. By replacing or supplementing traditional prototyping methods, digital prototyping empowers designers and engineers to explore ideas thoroughly without the constraints of physical production limitations.
Introduction to Digital Prototyping
Digital prototyping refers to the process of creating a virtual model of a product, system, or component that can be tested and analyzed using computer simulations. This technique has revolutionized the way products are developed by allowing teams to visualize, manipulate, and validate designs in a virtual environment before any physical prototypes are built. The significance of digital prototyping in modern design processes cannot be overstated, as it offers a dynamic platform for iterative development and innovation.
Compared to traditional prototyping methods, which often require significant time and resources to produce physical models, digital prototyping is inherently more cost-effective and time-efficient. Traditional prototypes involve manufacturing processes that can be expensive and time-consuming, particularly when multiple iterations are necessary. In contrast, digital prototypes can be modified quickly, enabling rapid iteration cycles that facilitate the refinement of designs in response to testing outcomes and stakeholder feedback. This efficiency not only accelerates the development timeline but also reduces the overall cost of bringing a product to market.
There are various types of digital prototyping, each serving specific purposes depending on the complexity and requirements of the project. Two-dimensional (2D) prototypes are commonly used for basic layout and conceptual designs, providing a simple visualization of the product's appearance and functionality. However, the most significant advancements have been made in three-dimensional (3D) virtual models, which offer a more comprehensive representation of the product. These 3D models allow for detailed analyses, including structural integrity, thermal properties, and fluid dynamics, providing insights that are critical for optimizing the design before physical production. By leveraging these different types of digital prototypes, designers can address potential issues early in the development process, thereby saving time and resources in the long run.
Benefits of Digital Prototyping
Reduced Time-to-Market
One of the most significant benefits of digital prototyping is the reduction in time-to-market. By utilizing virtual testing environments, design iterations can be accelerated substantially. Designers and engineers can perform tests and simulations rapidly, identifying potential flaws or areas for improvement without the need for physical models. This capability allows for rapid adjustments and updates based on feedback, ensuring that the final product meets the required specifications and customer expectations. The agility afforded by digital prototyping enables companies to respond swiftly to market changes and customer demands, maintaining a competitive edge in fast-paced industries.
Cost Savings
Cost efficiency is another critical advantage of digital prototyping. By minimizing material waste and production costs associated with building multiple physical prototypes, organizations can allocate resources more effectively. Physical prototyping often involves costly materials and labor-intensive processes, especially when dealing with complex designs or requiring multiple iterations. Digital prototyping eliminates much of this expense by allowing for extensive testing and refinement in a virtual environment. Additionally, the lower expenses associated with physical prototype development mean that companies can invest more in innovation and quality improvements rather than in the production of prototypes themselves.
Enhanced Collaboration
Digital prototyping also facilitates enhanced collaboration among cross-functional teams. Virtual models can be easily shared and accessed by team members across different departments and geographical locations, promoting real-time feedback and collective problem-solving. This accessibility ensures that all stakeholders, including designers, engineers, marketers, and clients, can engage with the prototype, provide input, and align their visions. The ability to collaborate seamlessly reduces miscommunications and errors, streamlining the development process and resulting in a more cohesive and well-refined product.
Key ways digital prototyping enhances collaboration include:
- Facilitating cross-functional collaboration with virtual models.
- Sharing prototypes across geographical boundaries for real-time feedback.
- Enabling synchronous and asynchronous communication among team members.
Tools and Techniques for Effective Digital Prototyping
Software Solutions
The effectiveness of digital prototyping largely depends on the software tools employed. There is a range of leading digital prototyping software available, such as Computer-Aided Design (CAD) tools and simulation software. These platforms offer robust features that support the creation of detailed and accurate virtual models. Key functionalities include real-time rendering and simulations, which enable designers to visualize how a product will perform under various conditions and stresses. By utilizing advanced software solutions, designers can create prototypes that closely mimic the behavior of the eventual physical product, providing valuable insights during the development phase.
Prominent software solutions in the industry include:
- CAD Tools: Software like Autodesk Inventor and SolidWorks facilitate intricate 3D modeling and design documentation.
- Simulation Software: Programs such as ANSYS and COMSOL Multiphysics allow for comprehensive testing of structural, thermal, and fluid dynamics aspects.
- Real-Time Rendering Software: Tools like Unity and Unreal Engine offer high-fidelity visualizations for immersive prototype experiences.
Techniques
In addition to software, various techniques are employed to create precise and functional digital prototypes. Methods such as voxel-based modeling and parametric design enable designers to build complex structures with high accuracy. Voxel-based modeling allows for the representation of objects in three-dimensional space using volumetric pixels, providing detailed control over the model's geometry. Parametric design, on the other hand, uses algorithmic thinking to encode relationships between design elements, enabling dynamic adjustment of the model's features based on specific parameters.
Validation processes through simulations are also a critical component of effective digital prototyping. Simulations for thermal dynamics, structural integrity, and fluid dynamics allow engineers to test how the product will perform under various operating conditions. For instance:
- Thermal Simulations: Predict heat distribution and identify potential overheating issues.
- Structural Simulations: Assess the product's ability to withstand mechanical stresses and strains.
- Fluid Dynamics Simulations: Analyze the flow of fluids around or within the product to optimize performance.
By incorporating these techniques, designers can identify and rectify potential issues early in the development process, ensuring a more reliable and efficient product.
Future Trends in Digital Prototyping
Integration with Emerging Technologies
The future of digital prototyping is being shaped by the integration of emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, augmented reality (AR), and virtual reality (VR). AI and machine learning are poised to significantly impact prototype refinement and optimization. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data from simulations and testing to identify patterns and suggest design improvements autonomously. AI-driven tools can optimize designs for performance, cost, and manufacturability, reducing the reliance on manual adjustments and accelerating the development process.
The role of AR and VR is also expanding in the context of digital prototyping. These technologies enhance user interaction with prototypes by providing immersive experiences. With AR and VR, stakeholders can virtually "walk around" or interact with a prototype in a simulated environment, gaining deeper insights into its functionality and ergonomics. This level of interaction facilitates better-informed decisions and can uncover issues that might not be apparent through traditional viewing methods.
Sustainability Considerations
Sustainability is becoming an increasingly important factor in the design and manufacturing industries. Digital prototyping supports the adoption of eco-friendly practices by reducing the need for physical prototypes, thereby conserving materials and reducing waste. Additionally, digital prototypes allow for lifecycle analysis and energy consumption modeling, enabling designers to assess the environmental impact of a product throughout its entire lifecycle. By simulating how a product will perform over time, companies can make informed decisions to improve durability, recyclability, and overall sustainability. As environmental regulations become more stringent and consumers demand more sustainable products, digital prototyping will play a crucial role in meeting these challenges.
Conclusion
Digital prototyping is undeniably transforming the design and development landscape. By leveraging virtual testing and validation, companies can accelerate innovation, improve efficiency, and enhance sustainability in their processes. The ability to iterate quickly, save costs, and collaborate effectively positions digital prototyping as an indispensable tool in modern design workflows. As emerging technologies continue to integrate with digital prototyping, its potential will only expand, offering even greater opportunities for optimization and creativity.
Designers and engineers are encouraged to adopt digital prototyping techniques to stay competitive in an evolving market. Embracing these tools not only enhances the quality of the products but also contributes to more sustainable and responsible manufacturing practices. In a world where time-to-market and innovation are critical success factors, digital prototyping offers a strategic advantage that can propel organizations to new heights in their respective industries.
Also in Design News
Subscribe
Sign up to get the latest on sales, new releases and more …