Your Cart is Empty
Customer Testimonials
-
"Great customer service. The folks at Novedge were super helpful in navigating a somewhat complicated order including software upgrades and serial numbers in various stages of inactivity. They were friendly and helpful throughout the process.."
Ruben Ruckmark
"Quick & very helpful. We have been using Novedge for years and are very happy with their quick service when we need to make a purchase and excellent support resolving any issues."
Will Woodson
"Scott is the best. He reminds me about subscriptions dates, guides me in the correct direction for updates. He always responds promptly to me. He is literally the reason I continue to work with Novedge and will do so in the future."
Edward Mchugh
"Calvin Lok is “the man”. After my purchase of Sketchup 2021, he called me and provided step-by-step instructions to ease me through difficulties I was having with the setup of my new software."
Mike Borzage
Advancements in Haptic Feedback: Revolutionizing Interaction in Virtual Design Environments
July 21, 2024 3 min read
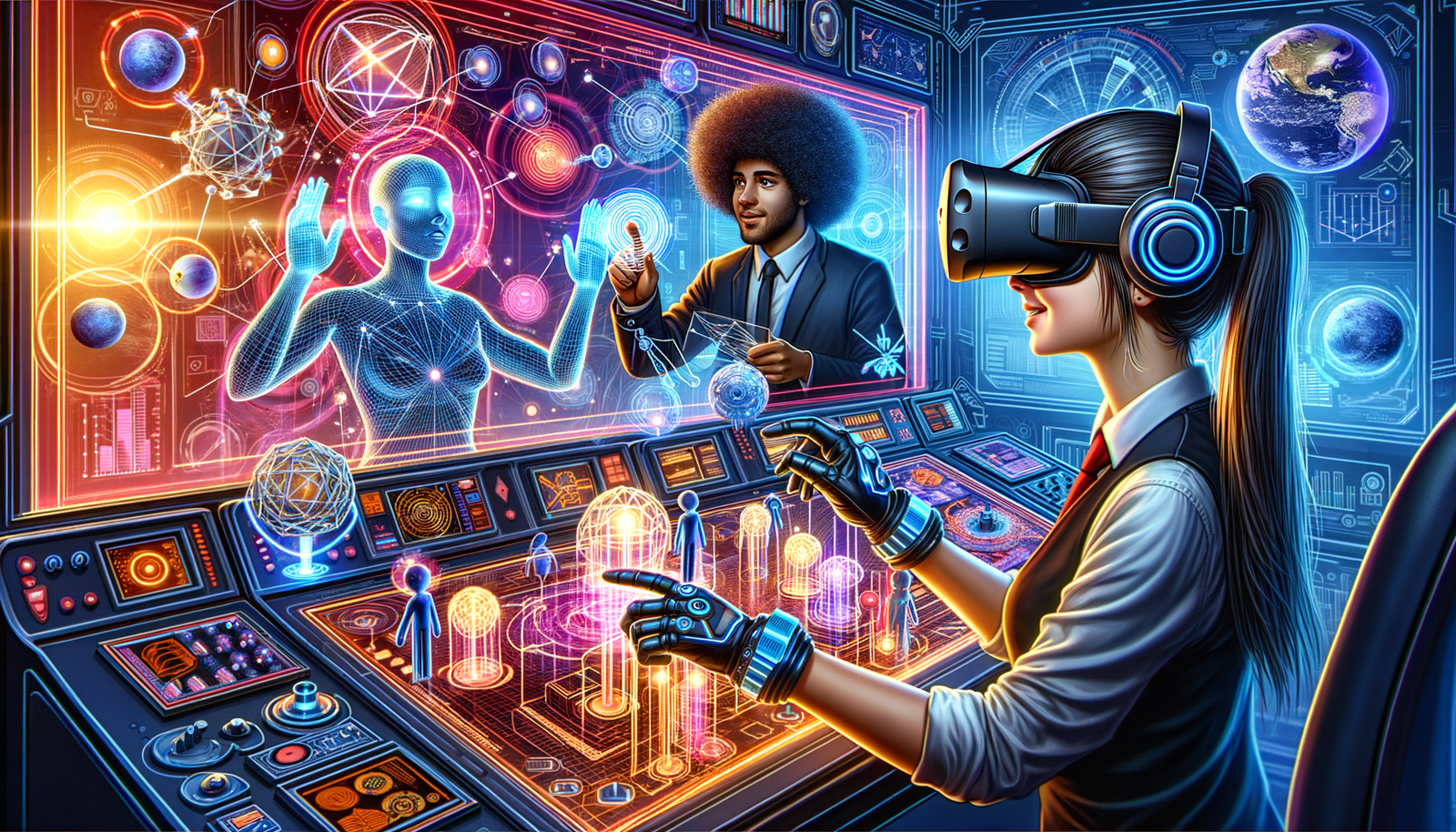


Exploring the Use of Haptic Feedback in Virtual Design Environments
Introduction to Haptic Feedback in Design
Haptic feedback, or haptics, refers to the use of touch sensation to communicate with users in a digital environment. Its application in virtual design environments marks a significant departure from traditional design methods, allowing designers to interact with virtual models in a more immersive, tactile way. This technology traces its roots back to robotics and teleoperation systems, with its evolution into the design sector being a relatively recent yet transformative development. The integration of haptic feedback into design software is changing how professionals engage with their creations, offering a more nuanced and interactive experience.
The Technology Behind Haptic Feedback
The essence of haptic technology lies in its ability to simulate the sense of touch through mechanical vibrations, forces, and motions applied to the user. This simulation is achieved through various devices such as gloves, vests, and styluses, which are designed to interact seamlessly with virtual environments and design tools. At the core of these experiences is sophisticated software capable of generating realistic touch sensations. This software interprets data from virtual models and translates it into tactile feedback, which poses significant challenges in terms of computational requirements and the accuracy of physical simulations.
- Gloves equipped with sensors and actuators to simulate texture and resistance.
- Vests that provide broader feedback for full-body immersion.
- Styluses that replicate the feel of drawing tools on different surfaces.
Applications of Haptic Feedback in Various Design Fields
The versatility of haptic feedback technology has enabled its application across a wide range of design fields, each benefiting from the unique advantages it offers in terms of interaction and immersion.
- Product design and prototyping: Designers can "feel" the surface and weight of a product, making adjustments before a physical prototype is ever produced.
- Architectural design: Architects have the ability to explore the texture of materials and understand spatial relationships within their virtual models, enhancing the design accuracy and decision-making process.
- Automotive design: Haptics facilitate ergonomics analysis by simulating the tactile response of vehicle controls and interiors, aiding in the development of more user-friendly cockpits.
- Medical device design: In medical training, haptic feedback plays a critical role in simulating surgical procedures, offering a realistic practice environment without the need for live subjects.
Future Trends and Potential Impact of Haptic Feedback in Design
As haptic technology continues to advance, its potential to revolutionize the design process grows. Emerging trends suggest a future where haptic feedback becomes a staple in design studios, offering unprecedented levels of detail and realism in virtual prototyping. The impact of these advancements is manifold, promising to enhance creativity, workflow efficiency, and collaborative opportunities across the globe. Particularly in the context of remote work, haptic feedback could serve as a bridge, enabling designers to share tactile experiences and insights regardless of their physical locations.
Predictions for the future of haptic feedback in design also highlight its potential role in education, where students could gain hands-on experience with materials, engineering principles, and design processes without the constraints of physical resources. Such developments, however, come with challenges, including hardware costs, computational demands, and the need for standardized protocols to ensure compatibility across different platforms and tools.
In conclusion, while the journey of integrating haptic feedback into design environments is still in its early stages, its transformative potential is undeniable. As technology progresses and obstacles are overcome, the role of haptic feedback in design is set to expand, reshaping how designers interact with their creations and setting a new standard for virtual design experiences.
Also in Design News
Design Software History: The Evolution of 3D Printing in Aerospace: From Prototyping to Production
November 27, 2024 7 min read
Read More
Cinema 4D Tip: Optimizing Workflow with Team Render in Cinema 4D
November 27, 2024 2 min read
Read MoreSubscribe
Sign up to get the latest on sales, new releases and more …



