Your Cart is Empty
Customer Testimonials
-
"Great customer service. The folks at Novedge were super helpful in navigating a somewhat complicated order including software upgrades and serial numbers in various stages of inactivity. They were friendly and helpful throughout the process.."
Ruben Ruckmark
"Quick & very helpful. We have been using Novedge for years and are very happy with their quick service when we need to make a purchase and excellent support resolving any issues."
Will Woodson
"Scott is the best. He reminds me about subscriptions dates, guides me in the correct direction for updates. He always responds promptly to me. He is literally the reason I continue to work with Novedge and will do so in the future."
Edward Mchugh
"Calvin Lok is “the man”. After my purchase of Sketchup 2021, he called me and provided step-by-step instructions to ease me through difficulties I was having with the setup of my new software."
Mike Borzage
Hybrid Simulation Pipelines: Integrating ROMs with CFD and FEA for Real-Time Design, Validation, and Governance
November 28, 2025 10 min read
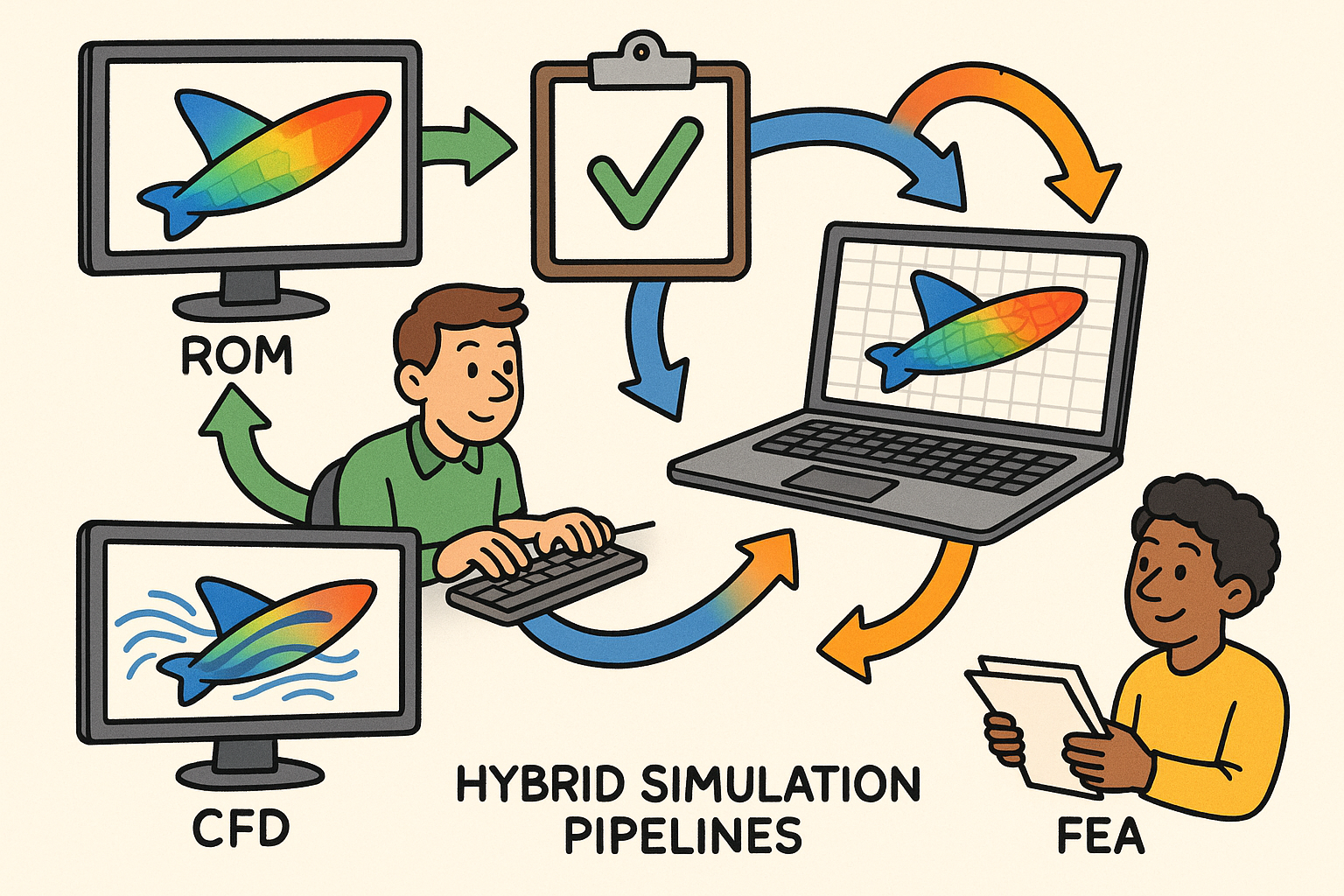

Why Hybrid Simulation Pipelines Now
Motivation
Design teams are converging on hybrid simulation pipelines because they compress iteration cycles without surrendering the physics that govern real performance. By blending high-fidelity solvers like CFD and FEA with reduced-order models (ROMs), engineers achieve an interplay of speed and rigor—using the right model at the right moment. ROMs, whether projection-based with hyper-reduction or data-driven operator surrogates, deliver interactive “what-if” exploration on the order of milliseconds to seconds. High-fidelity solvers, running locally or on the cloud, stay in the loop to validate, recalibrate, or fill gaps where nonlinearities spike. The result is a decision environment where a designer can alter geometry, materials, or boundary conditions and obtain an informed response in real time, with automated escalation to high fidelity if uncertainty grows beyond acceptable bounds.
- Blended fidelity compresses the loop from ideation to insight, enabling near-real-time evaluation of scenarios that used to demand overnight runs.
- Digital twins benefit from fast surrogates bounded by trust regions, so in-service decisions remain anchored to authoritative physics.
- Interactive dashboards tie ROM predictions to uncertainty indicators, prompting escalation to HF when error estimators exceed guardrails.
High-impact use cases
Hybrid pipelines shine when cross-discipline phenomena and latency budgets collide. For fluid–structure interaction (FSI), recurring aeroelastic evaluations—wing twist on UAVs, compliant valves, flexible rotors—can delegate the fluid interface to an aerodynamic ROM while structural dynamics run on an FEA ROM or high fidelity only at critical events. Conjugate heat transfer for electronics or e-mobility packs leverages transient CFD-on-GPU with a thermal-impedance ROM on the structure to accelerate trade studies involving fin geometry, TIM selection, or duty cycles. Thermo-mechanical distortion in additive manufacturing pairs a scan-strategy-aware heat source with a calibrated structural ROM to predict warpage and residual stress before build commitments. Control co-design scenarios—active aero, thermal throttling, or vibration suppression—benefit from loop rates under a few seconds, ensuring controllers “see” physics within their latency budgets while a background HF process validates corners that trigger instability.
- FSI: surrogate downwash or pressure loading feeds flexible-body solvers; strong coupling reverts to HF on detected divergence.
- CHT: compact thermal networks or impedance ROMs accelerate layout exploration while bounding maximum junction temperatures.
- AM: layer-wise thermal ROMs drive distortion predictions; selective HF re-simulates layers with extreme gradients.
- Control co-design: fast ROM plants ensure feasibility of controllers; scheduled HF replays vet robustness to disturbances.
Success metrics
Adoption should be governed by measurable outcomes. Latency and throughput determine whether design sessions remain interactive: ROM and CFD speedups should span 10–1000x while keeping error within specified bands. Fidelity guarantees hinge on error estimators and trust regions with auto-escalation to high-fidelity when surrogate confidence dips. Operational cost is tracked as HPC hours saved per program and cloud cost per design alternative, including data egress/storage. Robustness is assessed via stability under parameter shifts and graceful degradation: if a ROM leaves its design space, it reduces to a conservative mode or hands control to the HF solver with state reconciliation. These metrics create a shared language among engineering, management, and operations, ensuring the pipeline delivers durable value—not just impressive demos.
- Latency: sub-second queries for local sensitivities; 1–5 s for coupled ROM–HF updates; bounded tail latencies for worst-case events.
- Error envelopes: prediction intervals on key QoIs, with automatic HF verification when intervals widen.
- Cost: per-scenario wall-clock and cloud spend; incremental storage cost of snapshots and model artifacts.
- Robustness: stability rate across random parameter draws; success of rollback and replay mechanisms.
Architecture and Coupling Patterns
Partitioning strategies
Partitioning determines how and where ROMs enter the pipeline. Domain ROMs replace entire subdomains—for example, a reduced CFD volume around a wing or a reduced thermal solid for a battery pack—enabling high locality and large speedups. Interface ROMs approximate boundary operators, such as aerodynamic downwash, impedance, or admittance, preserving the high-fidelity solvers while accelerating coupling through compact boundary responses. Selection depends on how the physics localize: when interface behavior dominates and the bulk remains linear, boundary ROMs shine; when the subdomain is repeatedly queried across a design space, domain ROMs are compelling.
- Domain ROMs: best when mesh and topology are consistent across variants; parametric morphing keeps the basis valid.
- Interface ROMs: ideal for compact representations—pressure-to-displacement maps, heat flux-to-temperature impedance, or radiation view factors.
Another lever is frequency/time-scale separation. Fast, strongly nonlinear dynamics that defy compression remain high fidelity, while slow or parametric components are reduced. For instance, resolve a combustor’s unsteady hydrodynamics with HF on GPUs while a structural ROM captures slow thermal creep. By allocating fidelity per time-scale, you avoid overfitting ROMs to chaotic transients and capture long-horizon trends productively.
Coupling schemes
Coupling determines stability, accuracy, and latency. Monolithic schemes assemble a global system spanning physics; they are robust but expensive and less modular. Partitioned co-simulation employs separate solvers exchanging fields; it scales organizationally and computationally, at the cost of interface stability. Within partitioned schemes, explicit (staggered) coupling offers speed but risks instability for strong interactions, while implicit (strong) coupling—fixed-point or quasi-Newton iterations—is stable but increases per-step cost. The interface treatment matters: Dirichlet–Neumann and Robin couplings, augmented by Aitken relaxation or IQN-ILS quasi-Newton accelerators, tame oscillations without monolithic complexity. Robust time coordination uses adaptive subcycling, event-driven synchronization, and latency-aware scheduling to honor controller deadlines or streaming sensor cadences.
- Explicit step with safeguard: bounded under-relaxation and residual monitoring; auto-escalate to implicit when divergence flags.
- Implicit strong coupling: inexact Newton with interface Jacobian updates; terminate by QoI-based convergence criteria.
- Time integration: mixed-order stepping across solvers; event triggers on shocks, contact, or flow separation to re-grid or re-couple.
Data exchange and orchestration
Hybrid pipelines thrive on clean boundaries and predictable plumbing. FMI/FMU packages expose ROMs or even lightweight HF components to orchestration frameworks, standardizing initialization, stepping, and rollback. Industry bridges like CAPE-OPEN assist for process systems, while general-purpose functional mockups streamline deployability across desktop and cloud runtimes. Transport choices depend on coupling tightness: in-process calls for tight inner loops; gRPC or ZeroMQ for distributed elasticity; MPI for HPC nodes; shared-memory rings for GPU–CPU handoff where latency is paramount. Field exchange must be conservative: mortar methods maintain flux balances across nonmatching meshes, and RBF-based interpolation supports large deformations with smoothness. Surface and volume fields should carry named sets and functional annotations (e.g., “hot-side manifold,” “structural root”) so tooling can automate mapping and enforce intent-aware checks.
- Serialization: binary for inner loops; self-describing (XDMF/VTK) for audit trails; schema versioning to avoid silent drift.
- QoS: backpressure in message buses; prioritization for control-critical channels; bounded queue sizes to prevent latency creep.
- Observability: interface residuals, convergence progress, and timing histograms exported to dashboards.
ROM insertion and adaptivity
ROMs enter at two levels: projection-based with hyper-reduction and data-driven operators. Projection-based methods (POD–Galerkin, GNAT, DEIM/ECSW) compress PDE systems while preserving structure and, when designed carefully, conservation. They excel with parametric variations around a family of meshes and are amenable to error estimation. Data-driven surrogates—PINNs, DeepONet, operator inference—learn solution operators directly; they are powerful when geometry or physics libraries vary widely, provided training covers the operative manifold. Online error indicators and trust regions are non-negotiable: residual-based estimators, dual-weighted errors on QoIs, and classifier gates keep the ROM honest. When indicators trip, automatic model switching engages: the pipeline transitions from ROM to HF, reconciles state (via projection or filtering), and resumes with stronger coupling. Hybrid closures blend ML turbulence or constitutive models inside a CFD solver with a structural ROM, exploiting ML where closure data is rich while keeping the governing solution physics-based.
- Sampling: adaptive enrichment adds snapshots where residuals peak; operator retraining is staged for minimal downtime.
- State reconciliation: least-squares projection onto HF space with conservation constraints; low-pass filtering to avoid spurious oscillations.
- Safety: reject-and-retry on out-of-distribution detection; confidence-aware throttling of controller actions.
Performance engineering
Performance is a first-class design objective. Put CFD on GPUs where memory locality and stencil operations thrive; keep sparse structural solves on CPUs tuned for NUMA-aware placement, leveraging thread pinning to avoid cross-socket latency. Apply in-situ post-processing to compute QoIs without dumping massive fields. Checkpointing—at solver and orchestration levels—enables targeted rollbacks after unstable couplings, while deterministic replay reproduces bugs with cycle-level fidelity. Coalesced transfers minimize GPU–CPU shuttling; mesh LODs accelerate visualization without stalling compute. A performance budget should exist alongside error budgets: every microservice advertises latency percentiles and throughput; every ROM publishes flop and memory footprints; every field mapping reports conservation losses.
- Memory: struct-of-arrays for vectorization; page-locked buffers for DMA; async streams to overlap compute and communication.
- Scheduling: co-resident GPU kernels for CFD/ML closures; CPU cores reserved for orchestration to avoid priority inversion.
- Resilience: exponential backoff on failing transports; per-iteration watchdogs with automatic snapshotting for post-mortem.
Building, Governing, and Integrating ROMs in Design Software
ROM development workflow
High-quality ROMs start with disciplined data. Offline dataset curation uses a purposeful Design of Experiments across the parameter space, seeded by sensitivity analyses and augmented by active learning driven from residual or error indicators. Snapshots cover extremes and midpoints, and include controlled perturbations that test stability. Training and compression involve snapshot management, basis selection, and stabilization—especially for convection-dominated flows where naive projections oscillate. Hyper-reduction (DEIM/ECSW) prunes evaluations to selected points or elements. Enforce symmetries and conservation wherever possible: symmetry planes, periodicity, and balance constraints reduce data needs and improve extrapolation. For data-driven operators, embed physics priors via structure (e.g., divergence-free layers), loss terms (mass/energy), or PINN residuals that regularize the learned operator.
- DoE: Latin hypercube for broad coverage; targeted refinement near bifurcations detected by residual spikes.
- Stabilization: Petrov–Galerkin flavors for convection; shock sensors to modulate numerical diffusion in ROM space.
- Compression: greedy basis growth monitored by QoI error; snapshot SVD with energy thresholds tied to KPI targets.
Verification & validation
Verification assures we solve the reduced equations correctly; validation assures we solve the right equations for reality. Conduct k-fold validation across operating envelopes, holding out meaningful regime combinations to measure generalization. Where experiments exist, calibrate hyperparameters and boundary conditions with uncertainty quantified through Bayesian error modeling. Produce prediction intervals around QoIs, not just mean errors, and track how intervals evolve under temporal or geometric drift. Maintain a public ledger of test cases that represent the current design family and retired models. Most importantly, wire error estimation into runtime: if residuals or dual-weighted estimates exceed budget, the orchestrator escalates to HF or throttles control actions, logging the context for later ROM enrichment.
- Metrics: mean absolute percentage error per QoI; envelope coverage of prediction intervals; out-of-distribution rate per session.
- Calibration: hierarchical priors on closures; MAP fits with cross-validation; posterior predictive checks against time histories.
- Runtime gates: confidence thresholds trigger HF fallback; execution traces stored for reproducible analysis.
Model lifecycle and governance
A ROM is a living artifact and must be governed like source code. Apply semantic versioning tied to geometry, material, and boundary-condition revisions; embed provenance links to PLM/PDM so every result traces to its inputs. Continuous integration runs automated regression on key QoIs across a suite of micro and macro scenarios, with drift detection that flags retraining needs when passing thresholds. Guardrails are essential: unit tests for energy/mass conservation, monotonicity and positivity constraints for quantities like temperature or density, and safe fallbacks to high fidelity on violated invariants. Deployment policies should dictate who can promote a ROM from “experimental” to “verified” to “trusted,” each gate backed by test coverage, uncertainty documentation, and performance profiles. Governance is not bureaucratic overhead; it is a risk control that converts fast iteration into reliable engineering decisions.
- Provenance: hash geometry and mesh; store solver settings; record dataset fingerprints and training seeds.
- CI/CD: nightly regression on cloud; anomaly alerts to model owners; auto-open issues with failing traces.
- Policy: expiration dates for ROMs; mandatory revalidation after CAD feature edits affecting named sets.
Integration in CAD/CAE stacks
Integration succeeds when ROMs feel native to design workflows. Author ROM entries in a catalog attached to CAD features through named sets and functional annotations—“inlet plenum,” “battery tab,” “leading edge”—so co-sim configurations auto-map fields with minimal user friction. The co-sim UI exposes interface definitions, scheduling, and stability diagnostics, while dashboards stream QoIs with prediction intervals and error bars. Deployment spans desktop interactive studies, cloud batch ensembles, and edge runtimes backing digital twins where ROMs run in real time. Interoperability is vital: export/import FMUs, exchange fields in neutral formats (VTK/XDMF), and automate mesh LODs for fast loops. By encapsulating ROMs as portable components with rigorous metadata, you unlock repeatability and collaboration across teams, vendors, and compute substrates.
- Authoring: attach load cases and material variants to ROM applicability; specify trust-region bounds in units tied to CAD parameters.
- UI: latency and stability meters; “promote to HF” button for manual escalation; session logs that capture solver states.
- Deployment: desktop for sketches and tuning; cloud for design-of-experiments sweeps; edge for operations and anomaly detection.
KPIs and anti-patterns
Define KPIs with the same rigor used for cost or quality. Speedup versus high fidelity, wall-clock per scenario, error envelopes per QoI, compute utilization, and cost per decision compose a balanced score. Publish them on team dashboards so deviations spark conversation, not surprises. Beware anti-patterns that erode trust: ROMs wandering outside the design space without alarms; ungoverned data pipelines that silently change preprocessing; non-conservative field mapping that accumulates energy or mass errors; and ignoring latency budgets in FSI loops that destabilize controllers. Healthy pipelines include observability hooks and controls that make failure explicit and recovery routine. The objective is not perfection but controlled, transparent evolution—so that speed accelerates learning while guardrails protect outcomes.
- KPIs: p95/p99 latency, batch throughput per node-hour, conservation residuals, prediction interval coverage, retraining cadence.
- Anti-patterns: “black box” surrogates with no trust-region checks; monolithic meshes that block LOD and mapping diagnostics.
- Remedies: conservativity tests in CI; OOD detectors at runtime; budgeted HF verification quota per design gate.
Conclusion
What hybrid pipelines change
Hybrid pipelines deliver an order-of-magnitude speedup while preserving critical physics by combining FEA, CFD, and ROMs with discipline. They promote faster exploration without abandoning governing equations, and they create a bridge between interactive design, batch optimization, and real-time operations. Success hinges on robust coupling patterns that match physics interaction strength; conservative data exchange that respects flux balances; validated error bounds with trust regions; and automated model switching that escalates fidelity gracefully. Just as importantly, they elevate ROMs to first-class citizens: curated datasets, rigorous versioning, physics-enforcing constraints, and CI/CD pipelines convert models from promising prototypes into dependable tools that survive organizational change and scale. When approached holistically—architecture, performance, governance, and UI—the result is a design environment where insight is immediate, traceable, and operationally affordable.
- Blended fidelity marries interactivity with authority; you see results quickly and know when to verify deeply.
- Conservative interfaces and mesh mappings prevent hidden energy leaks that compromise long transients.
- Lifecycle governance turns ROMs into shared infrastructure, not ephemeral notebooks.
Practical first steps
Start small and intentional. Identify a high-impact interface—aerodynamic loading on a flexible component, a thermal impedance boundary in electronics, or a layer-wise heat source in AM—and wrap it as an FMU ROM with clear trust-region bounds. Instrument latency and error KPIs from day one, including residual-based estimators and conservation checks. Pilot a partitioned co-simulation with explicit coupling plus Aitken relaxation, and define escalation criteria that trigger HF verification. Bake governance into the pilot: version the ROM with geometry/material/BC provenance, run automated regression on a compact QoI suite, and publish dashboards that show prediction intervals and timing. When stability, latency, and governance are proven, scale outward to domain ROMs, richer couplings, and multi-site deployment. The path is incremental: each success adds a reusable component and a documented practice, compounding into a robust, fast, and trustworthy hybrid simulation capability.
- Pick one interface, one KPI, and one fallback, then iterate; resist boiling the ocean.
- Co-locate performance and error metrics in the same UI; operators should see both the number and its confidence.
- Plan for evolution: reserve budget for retraining and snapshot curation as the design envelope grows.
Also in Design News
Design Software History: From Rigid Trees to Constraint Networks: The Evolution of Parametric Assemblies in CAD
November 28, 2025 12 min read
Read More
Cinema 4D Tip: Prefer Instances Over Copies to Reduce Memory and Improve Viewport and Render Performance
November 28, 2025 2 min read
Read MoreSubscribe
Sign up to get the latest on sales, new releases and more …