Your Cart is Empty
Customer Testimonials
-
"Great customer service. The folks at Novedge were super helpful in navigating a somewhat complicated order including software upgrades and serial numbers in various stages of inactivity. They were friendly and helpful throughout the process.."
Ruben Ruckmark
"Quick & very helpful. We have been using Novedge for years and are very happy with their quick service when we need to make a purchase and excellent support resolving any issues."
Will Woodson
"Scott is the best. He reminds me about subscriptions dates, guides me in the correct direction for updates. He always responds promptly to me. He is literally the reason I continue to work with Novedge and will do so in the future."
Edward Mchugh
"Calvin Lok is “the man”. After my purchase of Sketchup 2021, he called me and provided step-by-step instructions to ease me through difficulties I was having with the setup of my new software."
Mike Borzage
Design Software History: The Evolution and Impact of STEP-NC in CNC Machining: From G-code Limitations to Advanced Manufacturing Standards
July 27, 2024 3 min read
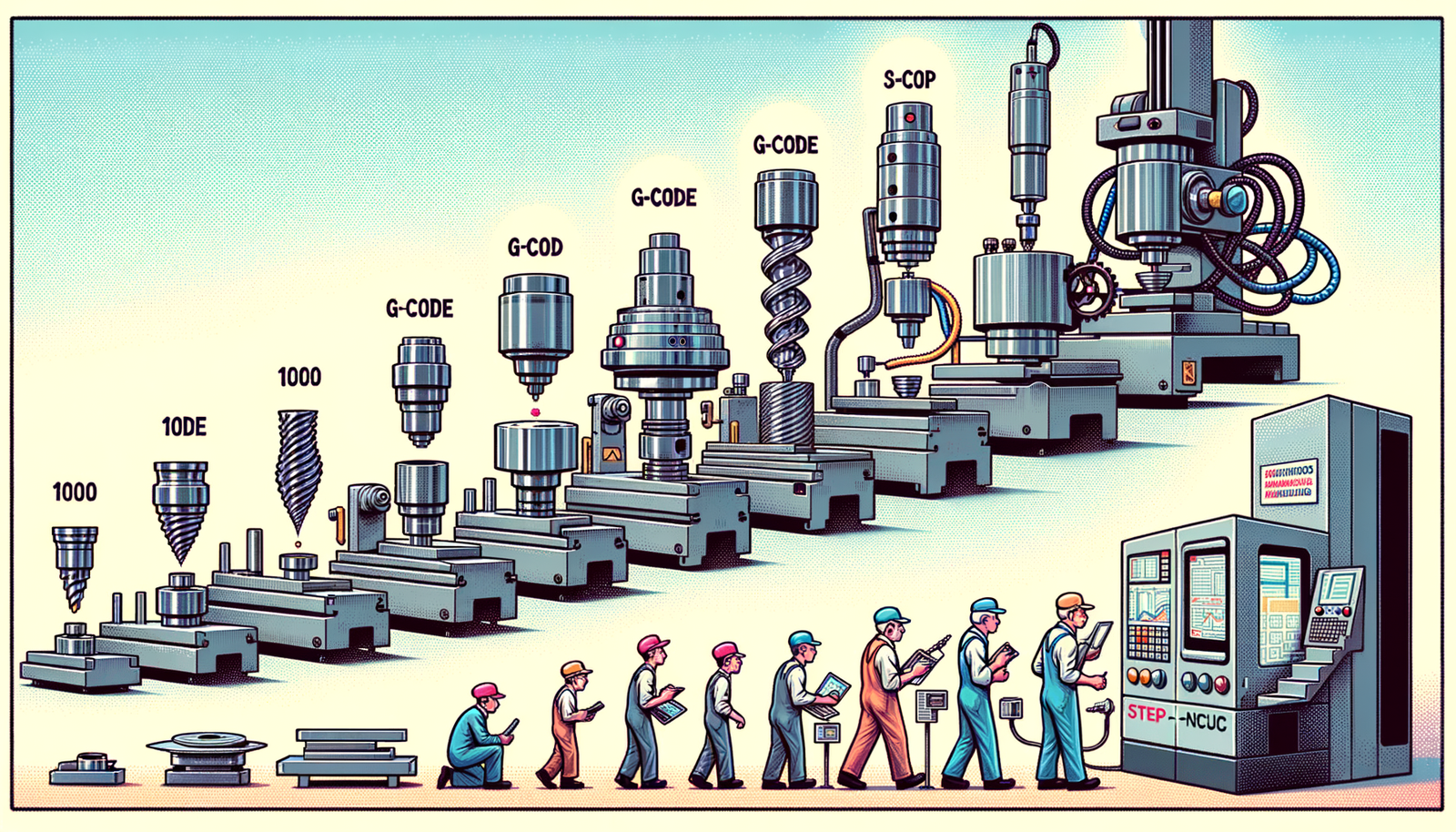

Introduction to the STEP-NC Standard
Overview of CNC Machining
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining has been a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, enabling the automated control of machining tools such as drills, lathes, mills, and 3D printers through computer programs. This technology is integral to achieving the precision and efficiency required in producing complex components with tight tolerances.
The Need for Enhanced Standards
Traditional NC (Numerical Control) standards, primarily G-code, have served the industry for decades but come with significant limitations. These include difficulty in handling complex geometries and a lack of interoperability between different machining systems. As manufacturing processes and product designs grew more sophisticated, the need for enhanced standards became evident.
Introduction to STEP-NC
STEP-NC (Standard for the Exchange of Product model data for Numerical Control) was developed to address these limitations. It aims to provide a richer and more comprehensive standard that integrates product and manufacturing information, thus enhancing the capability of CNC systems. The objective is to enable more efficient, accurate, and flexible machining processes.
Historical Context and Development
Early History of CNC and NC Standards
The concept of Numerical Control (NC) systems originated in the 1950s and 1960s. Early developments were driven by the need to automate machining processes for aircraft components. The emergence of G-code, a language for instructing CNC machines, marked a significant milestone. By the 1970s, G-code had become the dominant standard in the industry.
Challenges with G-code
While G-code was revolutionary for its time, it struggled with handling complex geometries and lacked the ability to ensure interoperability between different machining systems. These limitations became more pronounced as products and manufacturing processes advanced.
Initiation of STEP-NC Development
The development of STEP-NC began in response to these challenges. Key organizations, including ISO (International Organization for Standardization) and NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology), played crucial roles. Prominent figures like Dr. Martin Hardwick and Dr. Stephen Newman were instrumental in advancing the standard. Their contributions laid the groundwork for a new era in CNC machining.
Technical Foundations and Features of STEP-NC
Core Technology and Concepts
STEP-NC builds upon the existing STEP (Standard for the Exchange of Product model data) standard. This foundation allows for the integration of product and manufacturing information, providing a comprehensive dataset that includes geometric, topological, and manufacturing details. This integration is crucial for enabling advanced CNC capabilities.
Key Features of STEP-NC
- Associativity with CAD models: STEP-NC maintains a direct link between CAD models and machining instructions, ensuring consistency and accuracy.
- Enhanced data richness: It provides detailed information on geometry, topology, and manufacturing processes, facilitating more precise and efficient machining.
- Improved accuracy and flexibility: The standard allows for more accurate machining processes and greater flexibility in handling complex tasks.
Comparison with Traditional G-code
Compared to traditional G-code, STEP-NC offers significant advantages in terms of interoperability, precision, and data management. For instance, complex machining tasks that would be cumbersome and error-prone with G-code can be simplified and executed more accurately with STEP-NC.
Impact and Future Prospects
Adoption and Industry Impact
Major industries such as aerospace and automotive have begun integrating STEP-NC into their manufacturing processes. The benefits of using STEP-NC include improved production efficiency, reduced errors, and enhanced product quality.
Challenges in Adoption
Despite its advantages, the adoption of STEP-NC faces several challenges. These include technical barriers related to integrating the standard with existing systems, as well as organizational challenges such as training personnel and transitioning from legacy systems.
Future Developments and Innovations
Ongoing research and improvements in STEP-NC continue to push the boundaries of what is possible in CNC machining. The potential impact of AI and machine learning on CNC machining and STEP-NC is particularly promising, offering the prospect of even greater efficiency and sophistication in manufacturing processes.
Conclusion
In summary, STEP-NC represents a transformative advancement in CNC machining standards. Its ability to integrate product and manufacturing information, coupled with its advantages over traditional G-code, positions it as a key enabler of modern manufacturing efficiency and precision. As the standard continues to evolve, it promises to unlock new possibilities for the future of machining.
Also in Design News
RhinoArtisan: Discover the Power of Boutique by RhinoArtisan: Parametric Components
April 25, 2025 1 min read
Read More
💎 RhinoArtisan - Boutique: Design jewelry with your customer. In your store. In seconds.
April 25, 2025 1 min read
Read More
Integrating Additive Manufacturing with CAD: Revolutionizing Design and Production Workflows
April 25, 2025 7 min read
Read MoreSubscribe
Sign up to get the latest on sales, new releases and more …


