Your Cart is Empty
Customer Testimonials
-
"Great customer service. The folks at Novedge were super helpful in navigating a somewhat complicated order including software upgrades and serial numbers in various stages of inactivity. They were friendly and helpful throughout the process.."
Ruben Ruckmark
"Quick & very helpful. We have been using Novedge for years and are very happy with their quick service when we need to make a purchase and excellent support resolving any issues."
Will Woodson
"Scott is the best. He reminds me about subscriptions dates, guides me in the correct direction for updates. He always responds promptly to me. He is literally the reason I continue to work with Novedge and will do so in the future."
Edward Mchugh
"Calvin Lok is “the man”. After my purchase of Sketchup 2021, he called me and provided step-by-step instructions to ease me through difficulties I was having with the setup of my new software."
Mike Borzage
Design Software History: Evolution of Design Software in Smart Manufacturing: Key Technologies, Influential Figures, and Future Trends in Product Development and Production Processes
March 17, 2025 6 min read

Introduction
In today's rapidly evolving industrial landscape, smart manufacturing has emerged as a transformative approach that integrates advanced technologies to create highly flexible, efficient, and connected production systems. At its essence, smart manufacturing leverages digital information, automation, and data analytics to optimize manufacturing processes and supply chains. This paradigm shift is driven by the need to enhance productivity, reduce operational costs, and respond swiftly to market demands. The importance of smart manufacturing cannot be overstated, as it enables companies to remain competitive in a global market characterized by rapid technological advancements and shifting consumer preferences. Central to the success of smart manufacturing is the role of design software, which serves as the foundational tool enabling manufacturers to conceptualize, simulate, and optimize products and production processes before they are physically realized. Design software has evolved from simple drafting tools to sophisticated platforms that incorporate artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and the Internet of Things (IoT). These advancements have significantly expanded the capabilities of manufacturers to innovate and adapt. The objective of this article is to trace the evolution of design software within the context of smart manufacturing, highlighting the key technological advancements, influential companies, and pioneering individuals who have been instrumental in shaping its development. By exploring this evolution, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of how design software has become integral to modern manufacturing practices and its potential future trajectory in driving industry innovation.
Early Developments in Smart Manufacturing Design Software
The origins of smart manufacturing design software can be traced back to the advent of computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) and computer-aided design (CAD) in the 1970s and 1980s. This era marked a significant transition from manual drafting and machining to digital processes, laying the groundwork for the integration of computational technologies in manufacturing. A pivotal figure in this transformation was John T. Parsons, an engineer whose pioneering work in numerical control (NC) was instrumental in automating machine tools. In collaboration with the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), Parsons developed methods for controlling machining processes using punched cards, which allowed for precise and repeatable operations. This innovation was a cornerstone in the development of NC and later computer numerical control (CNC) systems, which became fundamental to modern manufacturing. Concurrently, leading technology companies like IBM, Siemens, and Dassault Systèmes began developing early software solutions that integrated CAD and CAM technologies. IBM's contributions included the development of mainframe-based CAD systems, which enabled engineers to create detailed digital models of products. Siemens advanced these concepts with their SINUMERIK control systems, integrating CAD/CAM functionalities and providing enhanced machine control capabilities. Dassault Systèmes revolutionized the industry with the introduction of CATIA (Computer Aided Three-Dimensional Interactive Application), a comprehensive software suite offering advanced modeling and simulation tools. CATIA became widely adopted in the aerospace and automotive industries due to its ability to handle complex geometries and facilitate collaborative design efforts. The integration of CAD and CAM technologies during this period facilitated a seamless transition from design to manufacturing, reducing errors, improving efficiency, and enabling the production of complex and precise components. These early developments were crucial in establishing the foundations of design software for smart manufacturing, setting the stage for subsequent technological advancements and deeper integration. The collaborative efforts of innovative individuals and companies during this era laid the groundwork for the sophisticated design tools that would become indispensable in modern manufacturing practices.
Technological Advancements and Integration
The progression of design software in smart manufacturing gained significant momentum with the emergence of the Internet of Things (IoT), introducing new dimensions of connectivity and data exchange. The IoT enabled machines, devices, and sensors within the manufacturing environment to communicate and share data in real time, enhancing the capabilities of design software through continuous feedback and adaptive control. This connectivity facilitated more responsive and efficient manufacturing processes, as data from the production floor could promptly inform design adjustments and optimizations. The incorporation of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning further expanded the functionality of design software. AI algorithms enabled predictive analytics and decision-making processes, allowing manufacturers to anticipate maintenance needs, optimize machine performance, and reduce downtime. Machine learning techniques allowed design software to learn from data, improving design recommendations and process optimizations over time. Key innovations during this period included:
- Integrated Software Suites: Development of platforms like Siemens PLM Software and PTC’s Windchill provided comprehensive solutions for product lifecycle management. These suites integrated design, simulation, manufacturing, and data management within a unified platform, enhancing collaboration and efficiency across different departments.
- Cloud Computing Integration: Adoption of cloud-based solutions allowed for scalable computational resources and global collaboration. Companies like Autodesk leveraged cloud computing in products such as Fusion 360, enabling real-time collaboration and access to advanced simulation tools without significant local hardware investments.
- Advanced Simulation and Modeling: Enhanced capabilities in simulation software allowed for more accurate virtual testing of designs under various conditions, reducing reliance on physical prototypes and accelerating the development process.
The Role of Modern Design Software in Smart Manufacturing
In the current era, design software has transcended traditional boundaries, becoming pivotal in orchestrating the entire smart manufacturing ecosystem. One of the most significant advancements is the implementation of digital twin technologies. A digital twin is a virtual representation of a physical product, process, or system used for analysis and simulation. By utilizing digital twins, manufacturers can perform virtual testing, predict performance issues, and optimize designs without the need for physical prototypes. This approach significantly reduces development time and costs while improving product quality. Modern platforms like Autodesk’s Fusion 360 and Siemens' NX provide robust digital twin capabilities, integrating real-time data from sensors and IoT devices to keep virtual models synchronized with their physical counterparts. Additionally, design software now supports real-time collaboration and iterative design processes, essential for keeping pace with rapid market changes. Cloud-based solutions enable teams across different geographical locations to work on the same projects, share insights, and make decisions collaboratively. This global collaboration accelerates innovation and allows companies to leverage a diverse set of skills and perspectives. Future directions in design software for smart manufacturing include:
- Integration of Blockchain Technology: Incorporating blockchain offers secure and transparent data flow across the manufacturing supply chain. This technology enhances protection of intellectual property and ensures data integrity, which is critical in collaborative environments involving multiple stakeholders.
- Focus on Sustainability: There is a growing emphasis on integrating renewable energy solutions and sustainable practices within smart manufacturing. Design software is adapting by incorporating tools that assess the environmental impact of products and processes, enabling companies to make more sustainable choices.
- Advancements in AI and Machine Learning: Use of generative design techniques and AI-driven optimization continues to expand. These technologies allow software to generate design solutions based on specified constraints and objectives, further enhancing innovation and efficiency.
Conclusion
The evolution of design software in smart manufacturing has been a journey of continuous innovation and integration. From the foundational work of pioneers like John T. Parsons and the early adoption of CAD/CAM technologies by companies such as IBM, Siemens, and Dassault Systèmes, to the sophisticated, AI-driven platforms of today, design software has transformed the way products are conceived and produced. This transformation has been fueled by advancements in technology, including IoT, AI, machine learning, and cloud computing, which have expanded the capabilities of design software beyond traditional boundaries. The critical role these technologies play in driving innovation and efficiency in manufacturing industries is evident. Design software enables companies to bring products to market faster, customize solutions to customer needs, and operate more sustainably. As we look to the future, the ongoing integration of emerging technologies like blockchain and a heightened focus on sustainability will continue to shape the landscape of design software. Manufacturers will increasingly rely on these tools to navigate the complexities of the global market, respond to technological developments, and meet evolving industry needs. In conclusion, the continuous evolution of design software underscores its importance as a catalyst for progress in smart manufacturing. By embracing these advancements, manufacturers can unlock new possibilities, drive innovation, and maintain a competitive edge in an ever-changing industrial environment.
Also in Design News
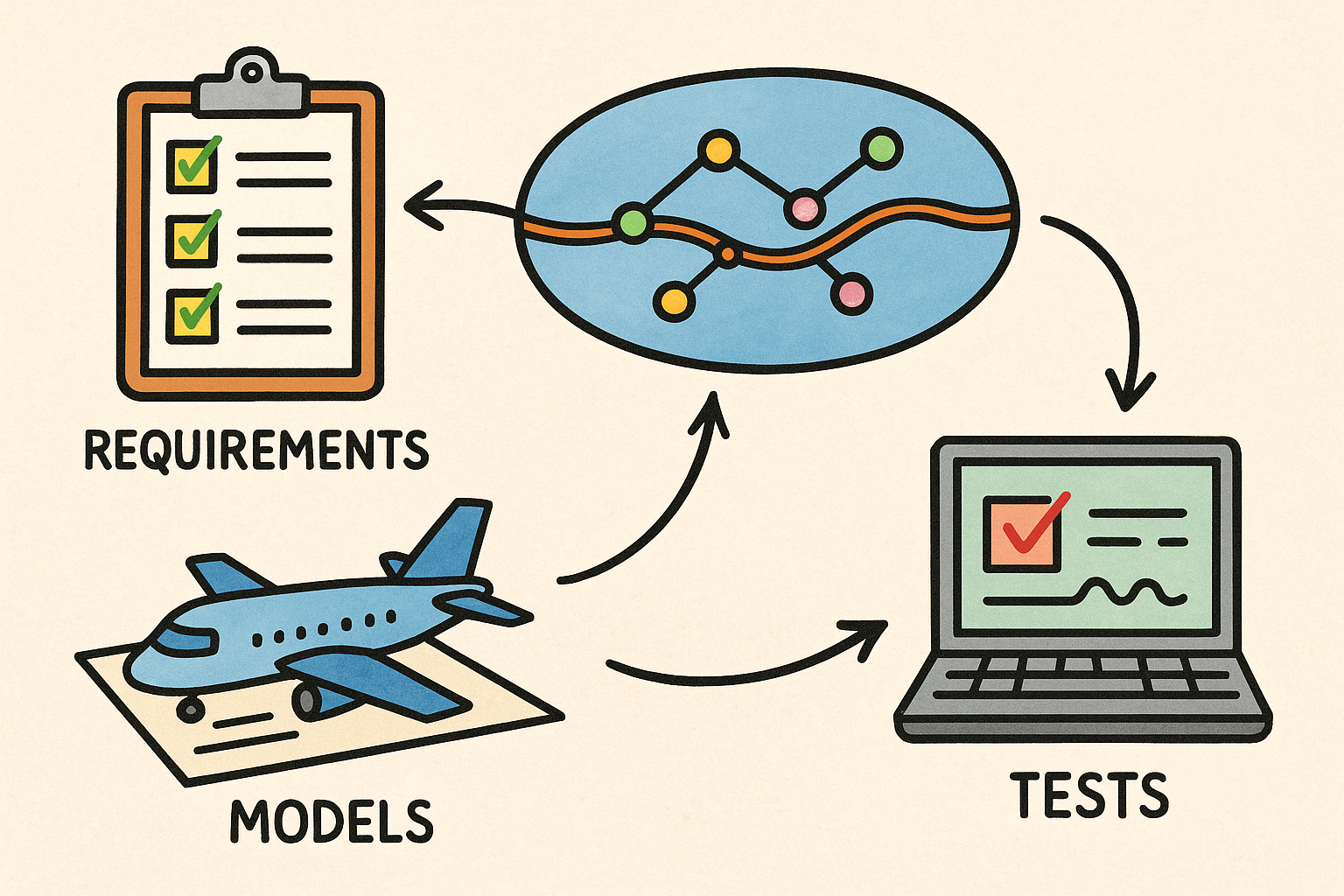
Semantics-First Digital Thread: Linking Requirements, Models, and Tests for Traceable Engineering
February 17, 2026 12 min read
Read More
Cinema 4D Tip: UV Tiling Best Practices for Cinema 4D and Redshift
February 17, 2026 2 min read
Read More
V-Ray Tip: Reflection Catcher Workflow for Photoreal Plate Integration
February 17, 2026 2 min read
Read MoreSubscribe
Sign up to get the latest on sales, new releases and more …


