Your Cart is Empty
Customer Testimonials
-
"Great customer service. The folks at Novedge were super helpful in navigating a somewhat complicated order including software upgrades and serial numbers in various stages of inactivity. They were friendly and helpful throughout the process.."
Ruben Ruckmark
"Quick & very helpful. We have been using Novedge for years and are very happy with their quick service when we need to make a purchase and excellent support resolving any issues."
Will Woodson
"Scott is the best. He reminds me about subscriptions dates, guides me in the correct direction for updates. He always responds promptly to me. He is literally the reason I continue to work with Novedge and will do so in the future."
Edward Mchugh
"Calvin Lok is “the man”. After my purchase of Sketchup 2021, he called me and provided step-by-step instructions to ease me through difficulties I was having with the setup of my new software."
Mike Borzage
Design Software History: Augmented Reality's Transformative Role in Construction Site Design and Visualization
November 23, 2024 7 min read
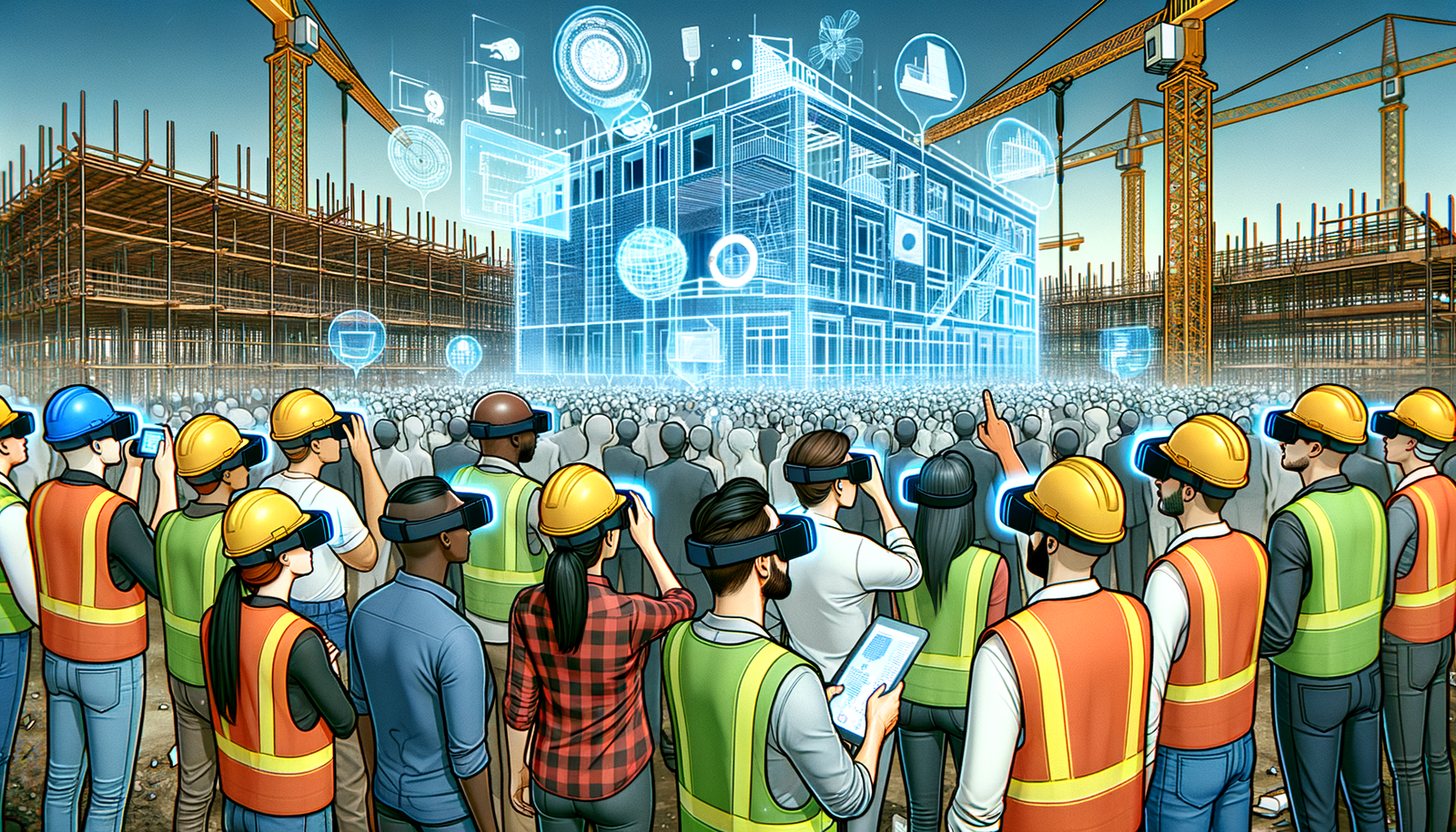


Introduction
Augmented Reality (AR) has emerged as a transformative technology in the realm of modern design processes, bridging the gap between digital and physical worlds. By overlaying computer-generated images onto a user's real-world view, AR enhances the perception of reality and provides designers with unprecedented tools to visualize and manipulate projects in real-time. The integration of AR into the design process has revolutionized how professionals in various industries conceptualize, present, and execute their ideas, leading to more efficient workflows and innovative outcomes. The relevance of AR in modern design cannot be overstated, as it enables a more interactive and immersive experience, fostering better communication and understanding among stakeholders.
The journey of AR technology began in the early 1960s with Ivan Sutherland's creation of the first head-mounted display system, known as "The Sword of Damocles." However, it wasn't until the advent of powerful mobile devices and advancements in computer graphics in the late 20th and early 21st centuries that AR started gaining significant traction. In the construction and design sectors, AR's potential was recognized as a means to visualize complex architectural plans and simulate construction processes before breaking ground. Early integrations of AR in these industries involved overlaying digital models onto physical environments, allowing architects and engineers to assess feasibility, detect possible conflicts, and plan more effectively.
Studying AR applications in construction site design is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it addresses the need for improved visualization tools that can reduce errors and enhance decision-making processes. By leveraging AR, designers and construction managers can interact with 3D models within the actual environment where a project will reside, leading to a more accurate understanding of spatial relationships and potential challenges. Secondly, the integration of AR promotes collaboration among multidisciplinary teams, enabling seamless communication and real-time problem-solving. Lastly, as the construction industry continues to evolve with technological advancements, staying abreast of AR applications ensures that professionals remain competitive and can deliver innovative solutions that meet the demands of modern urban development.
The Evolution of Augmented Reality in Design
The evolution of Augmented Reality in design has been marked by significant milestones that have propelled the technology from a conceptual novelty to a practical tool widely adopted across industries. The early research and development phases of AR were characterized by pioneering efforts in computer graphics and human-computer interaction. In the 1990s, researchers like Tom Caudell and David Mizell coined the term "Augmented Reality" while working at Boeing to develop a system that could assist workers in assembling aircraft wiring harnesses. This practical application showcased AR's potential in complex industrial processes.
As technology advanced, AR began to attract the attention of major companies seeking to explore its commercial applications. In the early 2000s, companies like Vuzix and Metaio (later acquired by Apple) developed AR glasses and software platforms that laid the groundwork for future innovations. The adoption of AR in various industries gained momentum with the introduction of smartphones and tablets equipped with advanced sensors and processing capabilities. This period saw tech giants like Google and Microsoft invest heavily in AR development. Google's Project Tango, launched in 2014, aimed to create mobile devices that could map 3D spaces, while Microsoft introduced the HoloLens in 2015, a mixed reality headset that blended holographic projections with the physical environment.
Notable figures such as Dr. Ronald Azuma, a pioneer in AR research, contributed to foundational studies that informed the design and functionality of AR systems. Startups like Magic Leap, founded by Rony Abovitz, pushed the boundaries of AR with significant investments in developing cutting-edge technology. The transition from theoretical applications to practical, user-focused solutions became evident as companies began to release developer kits and software development platforms, encouraging the creation of AR applications tailored to specific industry needs.
The construction industry, in particular, witnessed a growing interest in AR as professionals recognized its potential to enhance visualization and collaboration. Software companies like Trimble and Autodesk integrated AR capabilities into their design and engineering tools, allowing for immersive interactions with 3D models. The shift towards practical solutions was marked by the development of applications that could be utilized on-site, providing real-time data and visual overlays to assist in construction planning and execution.
- Early conceptualization and research by pioneers like Ivan Sutherland and Tom Caudell.
- Technological advancements in mobile computing and graphics processing enabling AR development.
- Investment by major companies such as Google, Microsoft, and Apple into AR hardware and software.
- Emergence of industry-specific applications and integration into existing design software platforms.
Applications of AR in Construction Site Design
Augmented Reality has significantly impacted construction site design by enhancing visualization and planning capabilities. By overlaying digital models onto physical environments, stakeholders can interact with proposed designs in a more intuitive and immersive manner. This technology allows architects, engineers, and clients to visualize complex structures in real-time, facilitating better understanding and feedback during the design phase. AR tools enable interactive site designs where users can manipulate elements, test different scenarios, and identify potential issues before construction begins. This proactive approach reduces the likelihood of costly errors and revisions, ultimately saving time and resources.
One of the key benefits of AR in construction site design is the improved stakeholder engagement it fosters. Traditional blueprints and 2D representations can be challenging for non-technical stakeholders to interpret. With AR, clients and team members can experience a virtual walkthrough of the construction site, gaining a clear and tangible sense of the project's scope and aesthetic. This enhanced visualization leads to more informed decision-making and aligns expectations among all parties involved. Moreover, AR assists in creating real-time visual overlays on construction sites, enabling professionals to compare planned designs with actual progress. This capability is crucial for identifying discrepancies between the design and the on-site execution, allowing for immediate adjustments.
The impact of AR on project management is equally profound. Utilizing AR for efficient site inspections and monitoring progress streamlines communication and coordination among project teams. Project managers can access real-time data and visual cues to assess the status of various construction phases, identify bottlenecks, and allocate resources more effectively. Collaboration tools that integrate AR technology facilitate remote consultations, enabling experts to provide guidance without the need for physical presence on-site. This is particularly beneficial for projects spanning multiple locations or requiring specialized input.
- Safety training and hazard identification: AR simulations can model dangerous scenarios, allowing workers to prepare and respond appropriately.
- Construction planning and sequencing: Visualizing the step-by-step process in AR helps in scheduling tasks and coordinating subcontractors efficiently.
- Maintenance and facility management: Post-construction, AR can be used to access building information models (BIM) for maintenance activities.
Future Trends and Challenges
The future of Augmented Reality in construction site design is poised for further innovation, driven by the integration of emerging technologies and the continuous quest for efficiency and accuracy. One of the most significant trends is the integration of AR with Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML). This convergence allows for more intelligent AR applications that can analyze data in real-time, provide predictive insights, and adapt to changing project conditions. For instance, AI-powered AR systems can recognize patterns, detect anomalies in construction processes, and suggest optimizations, thereby enhancing decision-making and reducing human error.
The potential for advanced data analytics and real-time feedback loops is another key trend shaping the future of AR in construction. By harnessing Big Data and IoT (Internet of Things) sensors, AR applications can present users with comprehensive dashboards that visualize critical project metrics. This real-time access to data supports proactive management, enabling teams to address issues promptly and maintain project timelines and budgets. Additionally, the development of more sophisticated AR hardware, such as lightweight wearable devices and headsets, will improve user experience and adoption rates.
However, several challenges hinder the widespread adoption of AR in construction. Cost barriers remain a significant concern, particularly for smaller firms that may not have the resources to invest in advanced AR technologies. The initial investment in hardware, software, and training can be substantial, making it difficult for these organizations to justify the expenditure without clear immediate returns. Moreover, the rapid pace of technological advancements can render equipment obsolete quickly, posing a risk for long-term investments.
Another critical area needing improvement is the lack of standardization and training in AR applications. The construction industry is fragmented, with various stakeholders using different tools and platforms. This lack of uniformity can lead to compatibility issues and hinder collaboration. There is a pressing need for industry-wide standards that ensure interoperability and streamline workflows. Furthermore, training and education are essential to equip professionals with the skills necessary to leverage AR effectively. Without proper training, the full potential of AR cannot be realized, and the technology may be underutilized or misapplied.
- Accessibility of technology: Ensuring that AR solutions are affordable and accessible to firms of all sizes.
- Development of industry standards: Creating guidelines and protocols for AR application in construction to facilitate collaboration.
- Education and training programs: Implementing comprehensive training to equip the workforce with necessary skills.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Augmented Reality stands as a pivotal technology reshaping construction site design and project management. Its ability to merge digital information with the physical world has unlocked new dimensions of visualization, collaboration, and efficiency in the design process. By enhancing how professionals interact with project models, AR has reduced errors, streamlined workflows, and fostered better communication among stakeholders. The significant impact of AR is evident in its widespread adoption and the continuous evolution of applications tailored to meet the complex demands of modern construction projects.
The potential for future growth of AR technologies in the design sector is immense. As advancements in AI, ML, and data analytics continue to integrate with AR, the capabilities of these systems will expand, offering even more sophisticated tools for designers and builders. The development of more accessible and user-friendly hardware will further drive adoption rates, making AR an integral part of standard design practices. The convergence of AR with other emerging technologies like IoT and cloud computing will create a comprehensive ecosystem where data flows seamlessly, enhancing decision-making and project outcomes.
The importance of ongoing research and adaptation cannot be overstated. The construction industry must remain agile and open to innovation to fully harness AR's capabilities. Investing in research and development will lead to new discoveries and applications that can address current limitations and challenges. Moreover, cultivating a culture of learning and adaptation within organizations will ensure that professionals are equipped to utilize AR technologies effectively. This includes implementing training programs, staying informed about technological trends, and participating in the development of industry standards.
In embracing AR, the construction and design sectors have the opportunity to revolutionize traditional methodologies, leading to more sustainable, efficient, and innovative practices. The journey towards fully integrating AR is ongoing, and with continued collaboration and commitment, the industry can achieve new heights of excellence in construction and urban planning.
Also in Design News

Design Software History: From Pen Computing to Pencil-First CAD: The Evolution of Mobile Design Tools, Kernels, and Cloud-Native Workflows
January 14, 2026 12 min read
Read More
Structure-Preserving Reduced-Order Models for Real-Time Control and Digital Twins
January 14, 2026 13 min read
Read MoreSubscribe
Sign up to get the latest on sales, new releases and more …